* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
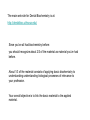
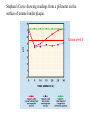
The main web site for Dental Biochemistry is at: http://dentalbioc.uthscsa.edu/ Since you’ve all had biochemistry before: you should recognize about 2/3 of the material as material you’ve had before. About 1/3 of the material consists of applying basic biochemistry to understanding understanding biological processes of relevance to your profession. Your overall objective is to link the basic material to the applied material. Biomolecules Pathways pH Glycolysis Caries Carbohydrates TCA cycle Fibrous proteins Amino acids Ox. Phos. Connective tissue Proteins Pentose phosphate Immunoglobulins Enzymes Gluconeogenesis Inflammation Lipids Glycogen Blood clotting Membranes Urea cycle Drug resistance AA metabolism Hemoglobin Nucleotide metabolsim Taste Lipid metabolism Hormones Replication Bones and teeth Transcription Nutrition Translation Diabetes Physiological processes Cancer Micrograph of a white spot lesion Erosion is sub-surface. Surface layer is yet to break through. Summary of processes involved in caries Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6 Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6 Stephan's Curve showing readings from a pH meter on the surface of enamel under plaque. Critical pH=5.5 pH and Tooth Decay • Tooth enamel is 96% mineral. • The mineral is primarily hydroxyapatite. • Hydroxyapatite is crystalline calcium phosphate. • Calcium phosphate is more soluble when the pH decreases (especially below 5.5): Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + 8H+ → 10Ca2+ + 6HPO42- + 2H2O • Some bacteria produce lactic acid when they metabolize sugars anaerobically. • Lactic acid produced by tooth-attached bacteria initiates most tooth decay by dissolving the mineral of enamel. Phosphate and Bicarbonate are the Major Buffers in Saliva -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Salivary Co mposition in Normal Adults -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Parotid Submand ibular Plasma pH 6.8-7.2 6.8-7.2 7.35 Flow Rate 0.7 0.6 (mL/mi n/gland) Potassium Sodium Chloride Bicarbona te Calcium Magnes ium Phospha te 20 23 23 20 2 0.2 6 mill imoles per li ter 17 21 21 18 3.6 0.3 4.5 4 140 105 27 5 2 2 pKa1= 6.1 pKa2= 7.2 Weak Acids as Buffers The titration curves of all monoprotic, weak acids have the same shape. The midpoint is at a pH value equal to the pKa value. plaque pellicle enamel Summary The objective is to envision your basic biochemical principles in the act of explaining how certain physiologic situations come about. Professors teaching the principles will help you out by interjecting some examples of the principles in action. Professors teaching about the physiologic situations will help you out by mentioning some of the principles at work. We will put some lectures about physiologic situations up front to establish what sorts of overall processes you are trying to understand. You can help yourself out by seeking as many connections as possible. Exemption Exam There is an exemption exam on July 25. If you can answer 80/100 multiple choice questions, you can exempt the course. To prepare for the exemption exam: Read this stuff first Introduction Intro. metabolism Caries pH Glycolysis Fibrous proteins Carbohydrates TCA cycle Connective tissue Amino acids Ox. Phos. Immunoglobulins Proteins Pentose phosphate Inflammation Enzymes Gluconeogenesis Blood clotting Lipids Glycogen Drug resistance Membranes Urea cycle Hemoglobin Replication AA metabolism Taste Transcription Nucleotide metabolsim Hormones Translation Lipid metabolism Bones and teeth Nutrition Diabetes Then ask how this stuff clarifies that stuff. Introduction Intro. metabolism Caries pH Glycolysis Fibrous proteins Carbohydrates TCA cycle Connective tissue Amino acids Ox. Phos. Immunoglobulins Proteins Pentose phosphate Inflammation Enzymes Gluconeogenesis Blood clotting Lipids Glycogen Drug resistance Membranes Urea cycle Hemoglobin Replication AA metabolism Taste Transcription Nucleotide metabolsim Hormones Translation Lipid metabolism Bones and teeth Nutrition Diabetes Test yourself using 2nd half of final exam from previous years.