* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
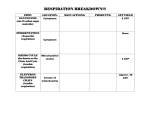
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Heterotrophs Vs. Autotrophs Autotrophs/ Producers-Make Their Own Food Using the sun’s energy (i.e. Plants) Heterotrophs/ Consumers-Obtain Energy From the food they eat (i.e. Animals) Production of Energy in heterotrophs Cellular Respiration – Process by which living organisms harvest energy from food they eat. C6H12O6 + O2 -> H2O + CO2 + energy(ATP) Do you notice anything about this equation? Forms of Respiration Oxygen gas makes the production of ATP very efficient. Although it is not required all of the time. Anaerobic respiration – The process of making ATP without the use of Oxygen. Aerobic respiration – The process of making ATP with the use of Oxygen. Cell Respiration Flow Chart Glycolysis Glycolysis – Break down of sugar in the cytoplasm. Glucose -> 2 pyruvates 2 ATP used + 4 ATP made 2 net ATP made Stage 2: Krebs Cycle The Krebs Cycle AKA The Citric Acid Cycle is a form of Aerobic Respiration. The Krebs Cycle requires the pyruvate and an NADH from Glycolysis, a CO2, and a molecule called Acetyl-CoA which is made from 1 pyruvate once it releases a CO2 molecule. Take home message! For each pyruvate made 2 3 1 1 CO2 molecules are produced. NADH molecules produced. FADH2 molecule is made. ATP molecule is made. How many ATP molecules are made per Glucose molecule? E.T.C. Between Glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle only 4 ATP molecules in total are made. Our body needs a total of about 36-38 ATP molecules. The rest come from an electron transport chain that gets the remaining energy from NADH & FADH2. The ETC also produces 2 water molecules that are released. The ETC makes a total of about 32-34 ATP. O2 is the final e- acceptor. E.T.C. Anaerobic Respiration Fermentation – A form of anaerobic Respiration that uses leftover NAD+ to make energy. Fermentation occurs when there is not enough O2. Being that O2 is the final e- acceptor from the e.t.c. an organism that is out of O2 needs to do something else for energy. There are two types of fermentation that you should know. Lactic Acid Fermentation After a cell goes through all of Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle if there in no O2 around it will not go through the E.T.C. The first type of fermentation produces a chemical called Lactic Acid. Humans go through this type of fermentation when their O2 level is depleted. When you exercise you’re forcing your body to work beyond the amount of O2 and energy that you have available to you. Your body will switch to fermentation to gain a quick burst of energy. C6H12O6 → 2 CH3CHOHCOOH (lactic acid) Alcoholic (Ethanol) Fermentation Another type of fermentation results in the production of Ethyl alcohol and CO2. An example of an organism that ferments is Yeast. C6H12O6 → C2H5OH (ethanol) + CO2