* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
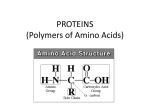
Chapter 4 Intro to Biochemistry Element: NA+, Cl-, S, O, H, C Atom: Intro to biochem. Continued.. Compounds: (chemically bounded) NaCl- sodium chloride *salt* H2O- water HCl- Hydrochloric Acid Mixture: (physically combined) –can be seperated Covalent Bond: 8e- “Marriage” 6e- 1e- 1e- Ionic Bonding: 1e- Give/Take “Partnership” 7 e- Substances can be divided up into acids, bases & neutral pH ScaLe! pH- measure of how acidic or basic a solution is STRONG ACIDS: corrode metals, buildings, living issue STRONG BASES: dissolve fats, grease, oil, clean drains, and are damaging to skin Organic compound composed of C, Hydrogen (H) & Oxygen (O) Polymer: any large molecule formed when smaller molecules combine. POLY: Many ISOMER: 1 molecule StruCture oF CarBoHydrATes! Structure: Carbohydrates are used to store and release energy in cells Monosaccharide- simple sugar. EX: glucose & Fructose Mono=1, saccharide= sugar Disaccharid-2 sugar carbohydrate. EX: glucose + Fructose = sucrose(table sugar) Polysaccharide- largest carbohydrate molecules. EX: starchpotato, bread Cellulose plants LiPiDs… Organic compounds with C-H bonds and less oxygen EX: Fats, oilsinsoluble in water, does not dissolve Cells use lipids for energy storage, insulation and protective coating EX: Large, complex polymer made of C, H, O and Nitrogen Provide structure and important for most functions in the body ¤ProTeiNs contin…¤ PROTEINS are made up of AMINO ACIDS: basic building blocks of proteins Amino Acids bond together by peptide bonds EX: Stores Cell information! Nucleic acids are made up of Nucleotides (building blocks) Structure: 3 main parts 1: a base 2: sugar 3: phosphate group Enzymes Most important type of protein found in all living things Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in digestion of food, storage, synthesis of molecules and much more! Catalysts: make reaction faster How They work: Each enzyme acts on a molecule called a Substrate. substrate LOCK The Substrate fits into an area of the enzyme called the active site. KEY Active site -> Active site-> Enzyme How they work contin. The enzyme holds the substrate in a position where a reaction can occur easily Enzyme/substrate Complex After the reaction, the enzyme releases the products and can go on to carry out another reaction (rxn) Product Enzyme (unchanged) Wine: grapes & yeast : wine! ^^ causes the sugar in the grapes to FERMENT-sugar is changed to carbon dioxide (CO2) & Alcohol (OH) Yeast contain enzymes ^^ Greek word means “in yeast” If you have: Milk + BacTerIa = Yogurt ^^ enzyme YoGurT L A B! In Lab: Milk + EnZymEs in = YoGurT (bactobacillus) What happens? -Enzyme converts sugar in milk to lactic acid & ^acid will Carbon Dioxide (CO2) cause milk to curdle & change into yogurt Cholesterol Cholesterol is a waxy steroid metabolite found in the cell membranes and transported in the blood plasma of all animals.[2] It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes, where it is required to establish proper membrane permeability and fluidity. In addition, cholesterol is an important component for the manufacture of bile acids, steroid hormones, and Vitamin D. Major dietary sources of cholesterol include cheese, egg yolks, beef, pork, poultry, and shrimp Hemoglobin Hemoglobin in the blood is what transports oxygen from the lungs or gills to the rest of the body (i.e. the tissues) where it releases the oxygen for cell use, and collects carbon dioxide to bring it back to the lungs. ©OpYriGht Chapter 4 By: Candi Marshburn