* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PBHS AP Biology
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
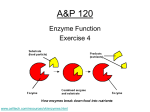
PBHS AP Biology STEVENSON 2009-10 Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Introduction: This the first of 12 AP Labs designed to illustrate the themes of this class. These labs are very important as the AP Test will have least one essay question and several multiple choice questions based on these labs. Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Introduction Enzymes are proteins produced by living cells that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions Substance to be acted on is called the substrate (S) The substrate binds reversibly to the active site of the enzyme (E) Reduces the energy required to activate the reaction so that products (P) can be formed E + S ES E + P Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Introduction The enzyme is not changed in any way and so can be recycled to break additional substrate molecules The active site is the portion of the enzyme that reacts with the substrate Any substance that blocks or changes the active site can affect the activity of the enzyme Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Salt concentration If the salt concentration is very low, the enzyme will denature and form an inactive precipitate If the salt concentration is very high, new interactions will occur and again an inactive precipitate is formed Intermediate salt concentrations such as human blood (0.9%) is the optimum for many enzymes Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis pH As the pH is lowered (solution becomes acidic), the side chains will attract H+ ions and the enzymes shape is disrupted As the pH goes up, the enzyme will lose H+ ions and again, the shaped is altered Optimum pH is in the neutral range At very low or high pH, the enzyme denatures (breaks down) Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Temperature Increasing temperature cause enzyme reactions to go faster… up to a point At very high temps, the enzymes structure is broken down Many enzymes function well up to 40-50 C, and some are active up to 70-80 C Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Activators and Inhibitors Many molecules other than the substrate may interact with an enzyme If such a molecule increases the rate of reaction, it is called an activator; if it decreases the rate of reaction, it is an inhibitor Many well know poisons such as potassium cyanide and curare are inhibitors that interfere with the active sites of critical enzymes http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalase Catalase was first noticed as a substance in 1811 when Louis Jacques Thénard, who discovered H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide), suggested that its breakdown is caused by a substance. In 1900, Oscar Loew was the first to give it the name catalase, and found its presence in many plants and animals. In 1937 catalase from beef liver was crystallised by James B. Sumner and the molecular weight worked out in 1938. In 1969 the amino acid sequence of bovine catalase was worked out. Then in 1981, the 3D structure of the protein was revealed. Hydrogen peroxide is a harmful by-product of many normal metabolic processes: To prevent damage, it must be quickly converted into other, less dangerous substances. To this end, catalase is frequently used by cells to rapidly catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into less reactive gaseous oxygen and water molecules Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Lab #2 The enzyme used in this lab is Catalase Catalase has 4 polypeptide chains, each composed of more than 500 amino acids One function of Catalase is to facilitate the breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) to H2O and O2 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 In the absence of catalase this reaction occurs spontaneously but proceeds very slowly The rate of the reaction can be measured in one of three ways Measuring the rate of disappearance of the substrate (H2O2) Measuring the rate of appearance of a product (O2 gas) Measuring the heat released or absorbed) Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Lab #2: General Procedure Read p 22 Exercise 2A: Test of Catalase Acvitity Exercise 2B: The Base Line Assay Exercise 2C: The Uncatalyzed Rate of H2O2 Decomposition Exercise 2D: An Enzyme-Catalyzed Rate of H2O2 Decomposition