* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Life
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Green chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
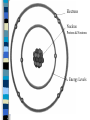
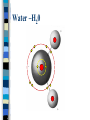
Chemistry of Life Chemistry of Life Matter -- anything that has MASS and takes up SPACE EVERYTHING matter is made of Chemistry of Life – the SMALLEST particle that can exist and still be considered matter Atoms All LIVING and NONLIVING things are made of atoms Atoms -- have three components ELECTRONS -- negatively charged PROTONS -- positively charged; found in nucleus NEUTRONS -- neutral; found in nucleus Electrons Nucleus Protons & Neutrons Energy Levels Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions occur when bonds are FORMED or BROKEN. This causes them to recombine into different substances. Chemical Reactions Metabolism – All reactions that occur in an organisms. These reactions break down and build molecules important to life. Chemical Reactions Mixture: – A combination of a substance in which the individual components contain their own property. Chemistry of the Cell Solution: – A mixture in which one or more substances are distributed evenly in another substance. Solvent: Solute: •A substance that •The substance can dissolve other that is dissolved substances pH Chemical reactions also depend on the pH of the environment within the organism. pH– A measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. pH The scale goes from 0-14 – 0 being the most acidic – 14 being the most basic Chemistry of Life Elements -- a substance that is made of only ONE kind of ATOM Reading Periodic Table Element Atomic Number Symbol The Human Body Major Elements of Life C = Carbon H = Hydrogen O = Oxygen P = Phosphorus K = Potassium Major Elements of Life I = Iodine N = Nitrogen S = Sulfur Ca = Calcium Major Elements of Life Fe = Iron Mg = Magnesium Na = Sodium Cl = Chlorine Chemistry of Life – matter that is made of more than one kind of ATOM Compounds are made by atoms sharing or taking ELECTRONS from other atom Compounds Inorganic Compounds Water ( H2O ) Each molecule is made of two HYDROGEN atoms and one OXYGEN atom Water –H20 Why is water so important to agriculture? At least 75% of animal body mass is water Plants contain 70-80% water Transports nutrients and wastes Why is water so important to agriculture? Dissolves compounds -“Universal Solvent” Regulates body temperature in animals Provides structure for plants Organic Compounds Organic Compounds contain carbon. Carbon forms the structural backbone of all living things. Carbohydrates Organic Compounds that contain: – Carbon – Hydrogen – Oxygen They provide energy Carbohydrates Three Types – Monosaccharides – Disaccharides – Polysaccharides Carbohydrates Monosaccharides – simple SUGAR – contain C6H12O6 – GLUCOSE, FRUCTOSE, AND GALACTOSE Carbohydrates Disaccharides – double SUGAR – contain two RINGS – SUCROSE and LACTOSE Carbohydrates Polysaccharides – complex CARBOHYDRATES – made of RINGS of SUGAR – STARCH, CELLULOSE, and GLYCOGEN Proteins Basic building material for all living things. Used for STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Made of H, O, C, N Structure of Proteins Amino Acids – building BLOCKS – 20 different kinds – all have the same elements but in different amounts Polypeptides – chains of AMINO ACIDS Joined by peptide bonds Proteins – chains of POLYPEPTIDES Used to make SKIN, HAIR, MUSCLE, ORGANS, etc. Lipids FATTY molecules used to store ENERGY Made of long chains of H & C followed by COOH Do not DISSOLVE in WATER Lipids have less OXYGEN than carbohydrates Examples of Lipids are: FATS, OILS, AND WAXES Nucleic Acids Store INFORMATION that controls CELL activities Made of a PHOSPHATE a SUGAR, and a BASE. Examples of Nucleic Acids are: DNA : – Deoxyribonucleic Acid The master copy of an organisms information code. Instructions to form all of an organisms structural proteins Examples of Nucleic Acids are: RNA : – Ribonucleic Acid This forms a copy of the DNA for use in making protein. Atoms are the building block of life!