* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
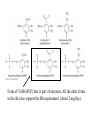
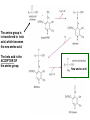
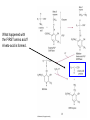
Vitamins and Minerals Sept 18, 2013 BIOCHEMISTRY OF VITAMIN B6 Form of Vit B6(PLP) that is part of enzymes. All the other forms in the diet also support the B6 requirement (about 2 mg/day). The RDA for adults, for B6, is 2 mg. Vitamin B6 is added to some foods (such as breakfast cereal). One serving TOTAL cereal meets the RDA; one serving of Cheerios is 25% of the RDA. By contrast, bakery products in the US are enriched with thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, and folate, but not usually B6. Good sources: chicken, beef, fish and other animal products. Bananas, potatoes with skin, collard greens, and some legumes, are also useful. Deficiency is not common in the United States. (The vegan diet may be somewhat low in B6) Milk is not a very good source (0.5 mg/quart) and the B6 is DEGRADED if milk is boiled to make formula; this may have caused infant seizures in the early 1950’s. Americans burn 100 grams of amino acids/day (derived from protein) for energy. That is 400 calories – sometimes 20% of total energy! What step is necessary, for those amino acids to be used for metabolic energy, such as the synthesis of ATP? Pyruvate, and every molecule in the TCA cycle, contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But amino acids all contain NITROGEN. What is the strategy that is used? MOST OF THESE CAN BE USED FOR ENERGY, IF THE AMINO GROUP IS REMOVED Donor amino acid The chemistry of transamination begins with the DONOR amino acid, which is going to provide the amino group. This is followed by a set of reactions with the enzyme, which we will discuss. Amino group from donor The amino group is is transferred to keto acid, which becomes the new amino acid. The keto acid is the ACCEPTOR OF the amino group. New amino acid What happened with the FIRST amino acid? A keto-acid is formed. AMINO ACID KETO ACID NEW KETO ACID NEW AMINO ACID Beside a new amino acid (GLUTAMATE), a new keto acid is formed (PYRUVATE). (the new keto acid, from reaction series #1). This reaction is done by the enzyme ALANINE TRANSAMINASE (ALT). What can be done with pyruvate, in metabolism? WE WILL DISCUSS THE DIAGRAM IN CLASS, WITH DETAILS ON THE BOARD After several weeks of HepA infections, there is a large release of alanine-transaminase (ALT) to the bloodstream, from damaged liver cells. What information does that provide about what’s happening inside the liver cell? Vitamin B6 (as PLP) is also a cofactor for the DECARBOXYLASE reaction. VITAMIN B6 IS REQUIRED TO CONVERT GLUTAMATE TO THE KEY NEUROTRANSMITTER, GABA. What could happen if there was a deficiency of B6? Plecko, et al, Human Mutation, 28: 19-26,2007 These patients require 100 mg/day of vit B6 to avoid seizures; the RDA is ~2 mg/day for healthy people with normal metabolism. Why do they require so much dietary B6? LYSINE CATABOLISM L-PIPECOLIC ACID ACCUMULATES – BECAUSE OF THE LACK OF THIS ENZYME Piperidine-6-carboxylate complexes with PLP, and creates a PLP “deficiency” A large amount of piperidine-6-carboxylate accumulates because of the enzymatic defect in lysine catabolism. In the brain, this makes a complex with B-6, and the brain has trouble making enough GABA. The result is seizures, because CNS function requires GABA. If these people are given very large doses of B-6 (100 mg/day), then enough is supplied to the brain to support GABA synthesis. There are a large number of disorders, each affecting small numbers of people, where those individuals require much larger amounts of a vitamin or mineral to maintain health, than do people without that metabolic disorder. This would be an interesting topic for class review. How common is B6 deficiency in humans? It’s one of the more widely-available B-vitamins, so deficiency does not seem to be a major public health problem (except of course for individuals with metablic problems, such as accumulation of pipecolic acid in the brain). In the early 1950’s, when formula was sometimes BOILED to achieve sterile baby food, there were some infants who had seizures. We know that mechanism, from the demonstrated role for B6 in sythesis of GABA. OTHER KEY ROLES FOR VITAMN B6: -synthesis of heme, starting with delta-aminolevulinic acid (B6-deficiency can contribute to anemia) -conversion of tryptophan to niacin -folate metabolism (Critical role!) -synthesis of several neurotransmitters THIAMINE DEFICIENCY MAY BE EASIER TO DIAGOSE THAN SOME OF THE OTHER MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES, BECAUSE LACTIC ACID ACCUMULATES IN THE BLOODSTREAM. LACTIC IS VERY EASY TO MEASURE ON A STANDARD CLINICAL CHEMISTRY ANALYZER From paper: Thiamine deficiency and acidosis Use of hemodialysis and bicarbonate is very standard if the causes of acidosis is renal failure! Thiamine-dependent steps in conversion of pyruvate to ATP Thiamine The first reaction (#1) requires thiamine to go forward. If this step is blocked, what happens to the pyruvate? Paper on Anorexia Nervosa: need to rely on “general symptoms” for diagnosis NIACIN DEFICIENCY CAN BE DIAGNOSED (WITH DIFFICULTY) BY A TEST FOR METABOLITES IN THE URINE. I CAN PROVIDE REFERENCES TO THIS PROCEDURE. WE CAN IN GENERAL CONCLUDE THAT DIAGNOSIS OF MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES IS A MAJOR CLINICAL CHALLENGE.