* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleotides and DNA Structure
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
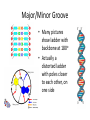
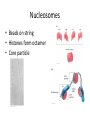
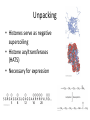
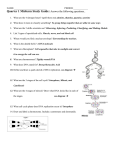
Nucleotides and DNA Structure C483 Spring 2013 1. Purine(s) which are found mainly in both deoxyribonucleotides and ribonucleotides are A) thymine and cytosine. B) cytosine and uracil. C) cytosine. D) guanine and cytosine. E) adenine and guanine. 2. The abbreviation dGp indicates A) 5' deoxyguanylate. B) 3' deoxyguanylate. C) 3', 5' deoxyguanylate. D) 5', 3'deoxyguanylate. E) dGMP 3. Much of the stability of the double stranded helical DNA structure is the result of A) hydrogen bonding between purines. B) the phosphodiester backbone. C) Ionic nucleobase attraction. D) the stacking interactions between base pairs. All five histones are rich in ________ amino acid residues whose positive charges allow binding to the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. A) lysine and alanine B) lysine and arginine C) leucine and alanine D) leucine and arginine Which does not apply to most bacterial DNA? A) Circular. B) Relaxed. C) Not packed into nucleosomes. D) Supercoiled. Which best describes the structure of a nucleosome core particle? A) A histone octamer with DNA threaded through its center. B) About 50 bp of DNA associated with one histone H1 molecule. C) One nucleosome plus one histone H1 and linker DNA. D) A histone octamer wrapped approximately two times around with DNA. Nucleic Acid Structure • • • • • • Nucleobase Nucleoside Nucleotide Nucleic acid Chromatin Chromosome Base Structure • Purines and pyrimidines • Aromatic • Tautomers • H-bonding Nucleosides • Ribonucleosides and deoxyribonucleoside • Purine = osine; pyrimidine = idine (watch cytosine) Nucleotides • Phosphorylated on 2’, 3’, or 5’ • 5’ unless noted • Draw these: – dA – ADP – ppAp – ApAp • pA is normally called _______ or _______________ Polynucleotides • • • • • Phosphate diesters polyanion directionality 5’ 3’ Abbreviation is pdApdGpdTpdC • tetranucleotide Double Stranded DNA • Chargaff’ Rule: %A =%T and %G = %C • (C + G) not necessarily equal to (A + T) Complementary Base Pairs Mismatching may occur with tautomers Antiparallel • Inaccuracy of twodimensional drawing: bases are perpendicular to the paper • “ladder” • H-bonding Helix • Maximization of base pair stacking • More compact • Major and minor groove • How do we explain major/minor grooves? Major/Minor Groove • Many pictures show ladder with backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side Weak Forces Stabilize Double Helix • Stacking interactions (vdW forces) • Hydrogen bonding • Hydrophobic effect • Charge-charge Denaturation • • • • Melting point Melting curve UV-absorption cooperative A/T Rich and G/C Rich strands • GC rich strands harder to denature due to STACKING (not H-bonds) • Cooperativity due to initial unstacking, which exposes bases to water, which destabilizes Hbonds, which leads to further denaturation Supercoiling • Bacterial DNA • Closed, circular DNA • Topology and topoisomerases Eukaryotic DNA • Chromatin • 8000x packing ratio – Nucleosomes (10x) – 30nm chromatin fiber (4x) – RNA/Protein scaffold holds loops (200x condensation of DNA length Nucleosomes • Beads on string • Histones form octamer • Core particle Unpacking • Histones serve as negative supercoiling • Histone acyltransferases (HATS) • Necessary for expression Chromosome • Scaffold of RNA and protein • 30nm fibers are looped many times • Picture of histonedepleted chromosome: DNA strands have fallen off of scaffold Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. E B D B B D