* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Macromolecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
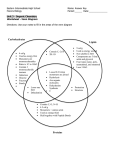
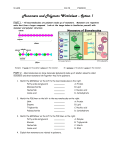
INTRO TO MACROMOLECULES “Macro”=BIG; Example: A protein may mass over 100,000 Daltons (amu) Compare to glucose: C6H12O6 = 180 Daltons Polymers made of monomers (subunits = identical or similar) Small molecules common to all organisms are ordered into unique macromolecule for individuals & species. Macromolecule Monomer 1. Carbohydrate = Monosaccharides 2. Lipid = Glycerol/Fatty Acids 3. Protein = Amino Acids 4. Nucleic Acid = Nucleotides Monomers are joined by Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation Synthesis); creates covalent bond. Water is removed from the monomers as they join = “dehydrate” the monomers. • 1 monomer provides the hydroxyl group (OH); the other monomer provides a Hydrogen (H) • Cell uses energy • Enzymes are used Ex. of Dehydration Synthesis Monomers are broken apart through Hydrolysis - (“hydro”= water; “lysis” = break/burst); reverse of dehydration synthesis. Water is used from the cell to hydrolyze the bond between the monomers; break bonds with water. The diversity of macromolecules in the living world is huge! The possible variety is effectively limitless. Why? CARBON!