* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A report published August 2006 demonstrated that peptide YY:
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
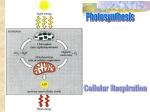
CQ 11-1 A report published August 2006 demonstrated that peptide YY: A - is upregulated by eating protein B - is a protein found in sperm C - is a protein that regulates male sexual behavior Announcements • Midterm Study – Focus on concepts in lecture (reading as supplement) – Online quiz – Downloads • Practice midterm without answers • With answers • Quiz key and study guide – URLs that might help you with studying • download section for Lec 13 • Discussion Philosophy Lecture 11: Cellular Respiration Monday 10/20/08 Reading Chapter 9 Pgs 162-180 Web Activities: 9.2, 9.4 Online Lecture 11 Quiz Fall 2008, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-1 Figure 6.10 The ATP cycle Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-2 • Mitochondria – Site of cellular respiration in all eukaryotic cells Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-3 Defects in mitochondrial function • Degenerative diseases, cancer, aging • Inherited mitochondrial diseases (1:4000 births) • Muscle weakness • Degenerative disease of the CNS • Metabolic disturbances marked by high levels of lactic acid Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-4 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Inherited mitochondria disorder QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Seizures: onset 1 month • Delayed gross and fine motor skill development • Generalized muscle weakness 3/25/98-6/9/03 Cellular Respiration • Relocation of electrons from food to oxygen – Released energy used to synthesize ATP • General redox reaction: – Two components • Oxidation- Removal of electrons from one substance • Reduction- Addition of electrons to a substance Reactants Xe- + Y X + Ye- Products Y will be reduced X will be oxidized Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-5 • Redox equation for cellular respiration Will be oxidized C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O will be reduced ATP • Glucose is oxidized (Hs and their electrons will be removed) to CO2 • Oxygen is reduced (Hs will be added) to H2O • Energy is released Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-6 Cellular respiration: controlled explosion Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-7 • NAD+ : Shuttles electrons from fuel to electron transport chain – Dehydrogenase enzymes strip 2 H atoms (2 electrons and 2 protons) from fuel • One H atom + 1 extra electron passed to NAD+ to form NADH • One H ion (H+ : proton minus electron) released to solution CC #11 With this hydroxyl containing molecule as fuel, complete the equation of the reaction described above. Circle the reactant molecule that will be oxidized? H - C - OH + ____ ______ + ______ + ___ Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-8 • NAD+ : Shuttles electrons from fuel to electron transport chain – Dehydrogenase enzymes strip 2 H atoms (2 electrons and 2 protons) from fuel • One H atom + 1 extra electron passed to NAD+ to form NADH • One H ion (H+ : proton minus electron) released to solution CC# 11 With this hydroxyl containing molecule as fuel, complete the equation of the reaction described above. Circle the reactant molecule that will be oxidized? Dehydrogenase H - C - OH + NAD _____+ ______ _____ + ____ C=O + NADH H+ Cellular respiration: NAD+ Tennis ball shuttle • NADH: moves electrons to transport chain Electron Transport Chain Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-9 • Cellular Respiration – Relocation of electrons from food to O2 – released energy used to synthesize ATP Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-10 EXTRACELLULAR Glucose Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-11 • Step 1: Glycolysis in cytosol – Converts glucose to pyruvate (used in citric acid cycle) – Generates 2 NADH, 2 H+ (used in oxidative phosph.) – Net gain of 2 ATP ( substrate level phosphorylation) – Requires initial energy investment Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-12 • Substrate level phosphorylation Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-13 QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Pyruvate moves into mitochondrial matrix – Aided by a transport protein For each pyruvate CO2 NADH Acetyl CoA Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-14 • Step 2 • Citric Acid Cycle: mitochondrial matrix – For each ACoA • 2 CO2 • 3 NADH • 1 FADH2 (another electron carrier) • 1 ATP Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-15 • Step 3 Electron transport chain: inner mito. Memb. NADH and FADH2 donate electrons Powers proton pumps, generates proton gradient Produces water Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-16 • Chemiosmosis: inner mitochondrial membrane Intermembrane space H+ H+ H+ H+ – The ATP synthase molecules allow passive transport of H+ – H+ flow through synthase results in joining of ADP+Pi to form ATP (chemiosomosis). H+ H+ H+ Inner membrane H+ ATP ADP+ Pi matrix Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-17 Cellular respiration generates 38 ATP/glucose Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-18 Pyruvate as a key juncture in catabolism In: Glucose,ATP Out: pyruvate,NADH, H2O, 2 ATP Ox Phos In: NADH, FADH2, O2 Out:H2O, ATP In: Acetyl CoA Out:NADH,FADH2 ATP, CO2 Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-19 Lactic Acid Fermentation Fall 2007, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-20 CQ 11-2 You have a friend who lost 15 pounds of fat from dieting. Where did the fat go? A) It was converted to water which weighs much less than fat B) It was converted to glucose, ATP produced, CO2 and H2O released C) It was converted to pyruvate and Acetyl CoA, ATP produced, CO2 and H2O released D) It was converted to amino acids and eliminated in the urine Lost 15 lbs of fat: A) It was converted to water which weighs much less than fat B) It was converted to glucose, ATP produced, CO2 and H2O released C) It was converted to pyruvate and Acetyl CoA, ATP produced, CO2 and H2O released D) It was converted to amino acids and eliminated in the urine Reading and Study Guide for Lecture 12 • Required reading – Chapter 10 pgs. 185-203 • Recommended exercises – Web Activities: 10.1, 10.2 Fall 2008, Bio 93, O’Dowd and Warrior, UCI - Copyright: All rights reserved 11-21 Oxidative Phosphorylation Demo Challenge: llustrate pumping ions across membrane, and having them flow back through synthase What I tried last year did not work and don’t have a good idea for this year