* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2
Metamaterial cloaking wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
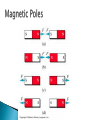
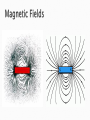
Mr. Fleming D4. Explain the relationship among voltage, current and resistance in a simple series circuit. D5. Explain how electricity is used to produce heat and light in incandescent bulbs and heating elements. D6. Describe the relationship between current and magnetism. What is a magnet? How does an object become magnitized? Magnetism ◦ The attraction of a magnet for another object. ◦ Discover 1,000s of years ago and referred to as lodestones. ◦ Certain part of lodestone or northern pole would always point to northern star called leading star Magnetic Poles ◦ A pole is an area of magnet where the magnetic effect is strongest. ◦ Two Poles North South Interactions between Magnetic Poles ◦ North + South= Magnets Attract ◦ North + North= Magnets Repel ◦ South + South= Magnets Repel Magnetism ◦ The force of attraction or repulsion between magnetic poles. Magnetic Field ◦ The region of magnetic force around each magnet ◦ Magnetic Lines Map out the magnetic fields around magnet. Spread out from one pole, curve around magnet, and return to other pole. Electron Spin ◦ The magnetic properties of a material depend on the structure of its atoms. ◦ Electrons are the particle that causes magnetism. Electrons spin as they orbit the nucleus. Moving electron produces magnetic field Magnetic Domain ◦ Clusters of billions of atoms that all have magnetic fields that are lined up in the same way. ◦ In a magnetized material all or most of the domains are arranged in the same direction. ◦ Domains are represented by arrows. Ferromagnetic Material ◦ A material that makes a good magnet. ◦ Iron, Nickel, Cobalt Making Magnets ◦ Place non-magnet near magnetic material. Destroying Magnets ◦ Drop, strike it hard, or heat it up. ◦ Domains knocked out of alignment. Breaking Magnets ◦ One broken magnet= two smaller magnets What is a magnet? A. Makes picking up paper clips easier. B. An object that has domains that are out of alignment. C. An object that only has one pole. D. An object that has two poles, and can attract other magnetic materials. D. An object that has two poles, and can attract other magnetic materials. How does an object become magnetized? A. B. C. D. It’s domains become misaligned. It’s domains become aligned in same direction. It needs to absorb more electrons. It needs to have a stronger south pole than north pole. B. It’s domains become aligned in same direction.























![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)


