* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4th grade Physical Science Part 2
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
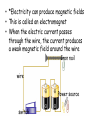
4th grade Physical Science Part 2 L.O. I will describe how magnets and electromagnets work. DAY 1 • Magnets will attract certain metals • Permanent magnet – an object that keeps magnetism for a long time • Temporary magnet – will lose magnetism after a short time • *Magnetic Poles – areas where the force of the magnet is greatest • *Bar and horseshoe magnets – pole is at the ends • Ring magnet – pole is on the face • *A compass is a free floating magnet that will always point North • *Like poles REPEL – push away S N N • *Opposite poles ATTRACT – pull together Magnetic Earth • Earth’s center is made up mostly of molten iron • As Earth spins, the iron particles line up, producing Earth’s magnetic field • *So Earth is like a gigantic bar magnet • *It is surrounded by a magnetic field with lines of force Day 2 • *Electricity can produce magnetic fields • This is called an electromagnet • When the electric current passes through the wire, the current produces a weak magnetic field around the wire Iron nail wire Power source switch – *To make the electromagnet stronger you can • *wrap more wire around the iron nail • *use more batteries or bigger batteries – If I take the batteries out or turn the switch off, the nail loses it magnetism • *Electrically charged objects will become a magnet and will either attract or repel • A motor will make a fan move • *An electric motor changes electrical energy into energy of motion • They use electromagnets and permanent magnets by using like poles to repel and the opposite poles to attract, making the motor move • *Electrical energy will convert to light, heat, and motion