* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECOLOGY PART I
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
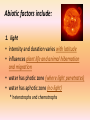
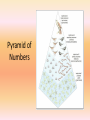
PART I Definitions: 1. Ecology = branch of biology that deals with interactions between organisms and their environment and interactions among organisms 2. biotic factors = living factors in the environment 3. abiotic factors = physical factors in the environment 4. limiting factor = physical factor in the environment that limits population growth Abiotic factors include: 1. light • intensity and duration varies with latitude • influences plant life and animal hibernation and migration • water has photic zone (where light penetrates) • water has aphotic zone (no light) * heterotrophs and chemotrophs Abiotic factors include: 2. temperature • varies with latitude and altitude 3. Water • precipitation varies region to region • varies with latitude and altitude • influenced by mountains and oceans Abiotic factors include: 4. soil and minerals • soil layers • topsoil – organic matter, living organisms, plant liter (humus) • subsoil – rock particles, mineral and nutrients • rock from bedrock below Biotic relationships: 1. populations • individuals of a certain species in an area • example = bullfrogs in a pond 2. community • different populations in a given area • example = bullfrogs, algae, fish in a pond 3. ecosystem • community and physical environment including biotic and abiotic factors Biosphere: portion of the earth’s surface where living things exist (about 20 km thick) includes: 1. lithosphere – solid surfaces of the earth 2. hydrosphere – water (on, under, and vapor over) 3. atmosphere – air mass Complete worksheet ECOSYSTEMS On page 2 in your packet Nutritional Relationships Autotrophic (producers) • Organisms that make their own food using CO2 • Most use photosynthesis, a few use chemosynthesis • This provides food for the heterotrophs Heterotrophs (Consumers) Organisms that cannot synthesize their own food 1. 2. 3. 4. Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Saprobes Herbivores • feed only on plants • rabbits, cattle, deer, sheep, horses Carnivores feed on other animals (meat eaters) • Predators –attack and kill prey (lions, hawks, wolves) • Scavengers – feed on dead animals that they find (vultures, hyenas) Omnivores • feed on plants and animals (bears, humans) Saprobes (decomposers) • organisms that obtain nutrients by breaking down remains of dead plants and animals (fungi and mushrooms) Predator – Prey Curve Predator population follows prey population Symbiotic Relationships • organisms that live in close association with each other and at least one benefits 1. Mutualism 2. Commensalism 3. Parasitism Mutualism: both organisms benefit • Termites and digestive organisms • Cows and digestive organisms • Lichens (algae and fungal cells) • Peas, clover, alfalfa (legumes) have nodules of bacteria on their roots that convert nitrogen gas into nitrogen in the soil that can be absorbed by the plants The alga provides food for the fungus, which then envelops the alga, providing shelter and nutrients. Commensalism one organism benefits and the other is not affected • Pilot fish and sharks • Barnacles on the body of a whale Parasitism one organism benefits and the other is harmed • Parasite and host • Can cause slight damage – some can kill • Tape worm in animals • Mistletoe and Indian pipe in plants Competition in ecosystems • Habitat – where an organism lives • Niche – role of the species in their ecosystem • When niches overlap –competition begins Intraspecific (within a species) Interspecific (between species) ENERGY FLOW 1. Food Chains 2. Food Webs Food Chains producer consumer consumer consumer (grass) (grasshopper) (frog) (hawk) Food Webs • Shows all of the food chains in a community Pyramid of Numbers Pyramid of Numbers TOP 3RD ORDER CARNIVORS 2ND ORDER 1ST ORDER HERBIVORS PRODUCERS GREEN PLANTS NUTRIENTS Lowest level is most numerous, most energy, most biomass 1. Numbers decrease going up the pyramid 2. Energy decreases going up the pyramid • Only about 10% of the total energy is passed level to level 3. Total biomass decreases going up the pyramid • Each level going up supports less numbers and less biomass 3rd level Consumer Secondary Consumers Primary consumers producers Complete worksheet ECOSYSTEMS On pages 6 and 7 in your packet