* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division Mitosis Cell cycle cancer
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
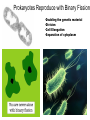
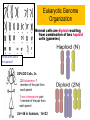
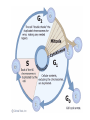
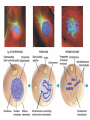
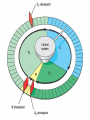
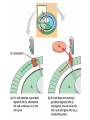
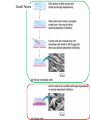
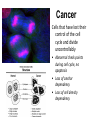
Asexual reproduction only one parent-reproduction without the fusion of gametes. Sexual reproduction is characterized by processes that pass a unique combination of genetic material to offspring, resulting in increased genetic diversity Prokaryotes Reproduce with Binary Fission •Doubling the genetic material •Division •Cell Elongation •Separation of cytoplasm Eukaryotic Reproduction More complicated Must organize more genetic material Clickers: 1. What process must occur prior to chromosome duplication? a. Cell reproduction b. Mitosis c. DNA replication d. Nuclear division Eukaryotic Genome Organization Normal cells are diploid resulting from combination of two haploid cells (gametes) What is the sex of this person? DIPLOID Cells, 2n 22 Autosomes -1 member of the pair from each parent 1 sex chromosome pair1 member of the pair from each parent 2n= 46 in humans, 1n=23 BEFORE we go further…. Homologous Pair corresponding genes, non identical DIPLOID Sister Chromatids one homologue doubled, identical Tetrad- both members of the pair doubled Mitosis Cell division that results in the EXACT duplication of parent cell into two daughter cells •Growth & Development Zygote to 10 trillion cells! •Asexual Reproduction –Making more of yourself; unicellular Think about organizing 6ft of DNA in tiny cell for every division! Growth Factors Cancer Cells that have lost their control of the cell cycle and divide uncontrollably • Abnormal check points during cell cycle, no apoptosis • Loss of anchor dependency • Loss of cell density dependency Cancer Karyotype