* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of the Cell Theory
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
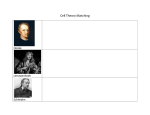
10/23/14 • Good Morning • Material Managers – please pass out folders • Take out your Cornell Notes (blanks are up front) • Label: Development of Cell Theory • FQ: How has our understanding of cells changed over time? 5 Scientists’ Contributions in the Development of the Cell Theory Hooke 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Development of the Cell Theory Hooke Development of the Cell Theory 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Van Leeuwenhoek 1. 1683 Used a simple microscope to observe pond water; “animalcules” 2. First to observe bacteria (from his own teeth scrapings!) Animalcules Hooke Development of the Cell Theory 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Van Leeuwenhoek 1. 1683 Used a simple microscope to observe pond water; “animalcules” 2. First to observe bacteria (from his own teeth scrapings!) Schleiden 1. “Botanist” who studied plants at a German university 2. In 1838 said, “All plants are made up of cells.” Hooke Development of the Cell Theory 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Schwann Van Leeuwenhoek 1. 1683 Used a simple microscope to observe pond water; “animalcules” 2. First to observe bacteria (from his own teeth scrapings!) Schleiden 1. “Botanist” who studied plants at a German university 2. In 1838 said, “All plants are made up of cells.” 1. studied frog larvae (animals) at same German university as Schleiden 2. 1839 concluded “All animals are made up of cells.” Hooke Development of the Cell Theory 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Virchow 1. Studied how a cell reproduces 2. 1855 stated, “All cells come from pre-existing cells.” Schwann Van Leeuwenhoek 1. 1683 Used a simple microscope to observe pond water; “animalcules” 2. First to observe bacteria (from his own teeth scrapings!) Schleiden 1. “Botanist” who studied plants at a German university 2. In 1838 said, “All plants are made up of cells.” 1. studied frog larvae (animals) at same German university as Schleiden 2. 1839 concluded “All animals are made up of cells.” Hooke 1. 1663 used compound microscope to observe cork slices. 2. Cork reminded him of rooms where monks lived. 3. Thus, coined term “Cell”. Development of the Cell Theory 1. Studied how a cell reproduces 2. 1855 stated, “All cells come from pre-existing cells.” Cell Theory 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function. 3. All cells come from other cells. Van Leeuwenhoek 1. 1683 Used a simple microscope to observe pond water; “animalcules” 2. First to observe bacteria (from his own teeth scrapings!) Virchow Schleiden 1. “Botanist” who studied plants at a German university 2. In 1838 said, “All plants are made up of cells.” Schwann 1. studied frog larvae (animals) at same German university as Schleiden 2. 1839 concluded “All animals are made up of cells.”