* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
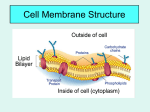
WARM UP #4 11/29 Yesterday you saw a plant and animal cell (yours). What 2 parts are 1. Only in plants? 2. Only in animals? 3. Do larger organisms = larger cells? 4. What is the purpose of the cell membrane? 5. What kinds of things do you think go into and out of the cell membrane in our cells? TODAY 11/29 1. 2. 3. 4. Learning Targets for the week Notes Ch 4 #2 Exploring Tonic Solutions Make a foldable LEARNING TARGETS 11/29 * I can explain 3 ways materials get into and out of the cell membrane to maintain homeostasis in the cell. * I can explain and predict what will happen in a hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic solution. NOTES Ch 4 #2 11/29 The cell membrane HOMEOSTASIS Maintaining a constant environment in the body Means: Our body wants to keep things the same or balance THINGS OUR BODY WANTS TO KEEP CONSTANT - Water balance Temperature Blood pressure pH (acid levels) Minerals Gases (O2 and CO2) CELLS play a big role in homeostasis CELL MEMBRANE – regulates what enters and leaves the cell SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE - allows only certain things and amounts in and out CELL MEMBRANE IS MADE OF 2 LAYERS There is rarely equal amounts of things on the inside and the outside of the cell. (like sugars, salts, water, fats, etc) CONCENTRATION GRADIENT Differences in amounts from one area to another Movement goes naturally from HIGH to LOW (where there is a lot to where there is a little) Example of concentration gradient If I sprayed a perfume at one end of the room, what would happen? Why would it happen? What if I did it and no one was in the room to cause any air movement? Example of concentration gradient If you put a drop of one thing into another, can they mix evenly without you mixing it???? What if I put a drop of dye into water? What will happen? • • EXPLAIN what happened? PASSIVE TRANSPORT - movement of particles WITH the concentration gradient - high to low (or from a lot to a little) Sometimes things need to get in where there is not a lot…. It needs to go backwards ACTIVE TRANSPORT – movement of particles AGAINST the conc gradient low to high (or from little to a lot) What kind of transport – active or passive and why? * Uses energy to do this, more work How do materials get in and out? 1) pushing through membrane (large) 2) through protein “pumps” in the membrane (sugar and salts) 3) Go right through the membrane (water and gases) a) Diffusion – movement of particles from high to low a) Osmosis – diffusion of water What were the 3 ways that things get into a cell? • Push • Protein Pump • Go right through What were the two types of transport? • Active • Passive Our cells are always in a solution….. What is a solution? SOLUTE - material that gets dissolved + SOLVENT - liquid that does the dissolving = SOLUTION – mixture of solvents and solutes 1 3 2 Blood is a solution of what? Urine is a solution • What are some other solutions in our body? Our cells are a solution! Examples of solutes that go into and out of our cell Gases (O2, CO2) Fats (lipids) Sugar Salts Calcium Hormones Enzymes Back to our dye example earlier… Cells are in solutions, but not always even 3 TYPES OF OSMOTIC (water) SOLUTIONS OUR CELLS CAN BE IN: Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic DO NOT WRITE One type will keep things the same One type will cause cells to swell or burst One type will cause to shrink or shrivel How does this work????? EXPLORING the TONICS GROUPS OF TWO (see worksheet) Have pictures of iso, hypo, and hyper tonic solutions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. What do you notice is different about the 3 solutions? Which solution has a higher concentration of water inside the cell? What do you would predict would happen to the cell in this type of environment? Which has a higher concentration of water outside the cell? Would water flow into or out of the cell? What do you predict would happen to the cell in this type of environment? Would water flow into or out of the cell? If a person is lost at sea and drinks the salt water, what type of solution would his body be in? Explain what would happen to him. Predict what would happen to a cell that is 70% water being placed into a 30% water solution. Draw a diagram showing this. Predict what would happen to a cell that is 70% water being placed into a pure water solution (100%). Draw a diagram showing this and label what type of tonicity it is. Why would a person studying to be a nurse need to know about this? What would they need to do to a person that is coming in the hospital dehydrated – what kind of solution of IV would they need to give them? DESIGN AN EXPERIMENT You want to know if what you just learned is true, so you are going to design an experiment to test hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic. Given – 3 cells that are 65% water MATERIALS? EXPERIMENT? (step by step) ISOTONIC Hypertonic Hypotonic Hemolysis – the rupture of red blood cells Due to the blood cell being placed in a pure water solution - the pure water will go into the blood cell (hypotonic solution) and cause it to burst Crenation – the shrinking of red blood cells If red blood cell is placed in a very concentrated solution of a chemical (EX: very salty) then the water in the cell wants to leave to where there is less concentration of water. Cell will shrink