* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio-Ch-8-Mouse
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
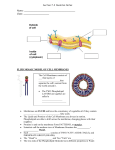
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 REVIEW Mouse Mischief Which of the following best describes the cell membrane waterproof layer of sugars connected to surface protein single layer of amino acids double layer of phospholipids thick layer of glycoproteins What is the difference between passive transport and active transport? Passive transport requires energy, and active transport does not. Active transport requires energy, and passive transport does not Passive transport uses carrier proteins, and active transport does not. Active transport uses carrier proteins, and passive transport does not The discharging of materials to the outside of a cell using vesicles is called exocytosis endocytosis. passive transport channeling proteins. When a receptor protein in a cell membrane acts as an enzyme, the receptor protein changes its shape to allow the signal molecule to enter the cell. triggers a chemical reaction in the cell activates a second messenger that acts as a signal molecule within the cell. changes the permeability of the cell membrane. When a particle moves across a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration, the cell is using diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis active transport Receptor proteins have binding sites, each with a unique shape because the outer amino acids fold in a complex pattern the inner amino acids arrange themselves in a dense ball. vesicles change the shape of the cell membrane. these proteins can respond to light from the environment Which of these are the two categories of transport proteins? receptor proteins and glycoprotein glycoproteins and channel proteins channel proteins and carrier proteins carrier proteins and receptor proteins Why are phospholipids ideal for making up the selectively permeable cell membrane? They repel small ions They react readily with water molecules. They form triple layers that insulate the cell They have a nonpolar and a polar region. The membrane-bound proteins that identify a cell type are enzyme glycoproteins receptor proteins. transport proteins Which substance crosses the cell membrane by facilitated diffusion oxygen sugar sodium ion chloride ion The concentration of molecule X is greater inside a cell than it is outside the cell. If the cell acquires X from its surroundings, X must cross the cell membrane by means of exocytosis. active transport. receptor proteins second messengers A cell begins to swell when it is placed in an unknown solution. What can you conclude about the solution? The solution is isotonic The solution is hypotonic The solution is saturated The solution is hypertoni Which proteins transmit information into a cell by binding to signal molecules end protein marker proteins channel protein receptor proteins What will happen to a cell (1% salt) that is placed in a 5% salt solution? Salt moves in Salt moves out Water moves in Water moves out Osmosis Lab: Which potato cube lost water to the NaCl solution? Which of the following is a characteristic of active transport? It moves substances against a concentration gradient. It requires energy from the cell Both (a) and (b) Diffusion is the movement of a substance through only a lipid bilayer. only in liquids from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration If the concentration of a sugar solution is lower outside the cell than inside the cell, which of the following will happen by osmosis? Sugar will move into the cell Water will move into the cell. Sugar will move out of the cell An ion channel is a transport protein that moves substances against a concentration gradient pumps ions only out of a cell. serves as a tunnel for specific substances. Molecules that are too large to be moved through the cell membrane can be transported into the cell by osmosis endocytosis exocytosis. second messenger binds only to the signals that match the specific shape of its binding site chemical that carries information to cells acts as a signal molecule within the cell unique shape of the outer part of a protein binding site binds only to the signals that match the specific shape of its binding site chemical that carries information to cells acts as a signal molecule within the cell unique shape of the outer part of a protein receptor protein binds only to the signals that match the specific shape of its binding site chemical that carries information to cells acts as a signal molecule within the cell unique shape of the outer part of a protein signal binds only to the signals that match the specific shape of its binding site chemical that carries information to cells acts as a signal molecule within the cell unique shape of the outer part of a protein Which cell is in a hypertonic solution? Which cell is in a hypotonic solution? Which cell is in a isotonic solution? Which part(s) of the lipid bilayer is polar? Which part(s) of the lipid bilayer is nonpolar? Which part of the cell membrane identifies the cell type? phospholipid bilayer receptor proteins transport protein cell-surface markers Which of these statements is true about the cell membrane? The outer surfaces are polar, while the interior is nonpolar The outer surfaces are nonpolar, while the interior is polar. Polar and nonpolar regions are randomly arranged throughout the membrane. A layer of water within the membrane causes the membrane to form as a lipid bilayer. By controlling what enters and leave a cell, the cell membrane aids in maintaining homeostasis within the cell. aids in maintaining homeostasis outside of the cell. aids in maintaining osmosis within the cell. aids in maintaining osmosis outside of the cell Which kind of molecules can pass unaided through the cell membrane? small, polar molecules small, nonpolar molecules polar molecules of a specific shape nonpolar molecules of a specific shape Diffusion is the movement of a substance only in liquids. through only a lipid bilayer. down its concentration gradient. against its concentration gradient. When particles move out of a cell through facilitated diffusion, the cell gains energy uses energy. first gains and then uses energy. does not experience any change related to energy. The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called endocytosis exocytosis. osmosis isotonic movement Molecules that are too large to be moved through a cell membrane can be transported into the cell by osmosis endocytosis exocytosis. membrane proteins. If the concentration of a sugar solution is lower outside the cell than inside the cell, which of the following will happen by osmosis? Sugar will move into the cell. Water will move into the cell Water will move out of the cell Both (a) and (c) What is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump? to remove sodium from a cell, against its concentration gradient to remove potassium from a cell, against its concentration gradient to remove sodium from a cell and bring potassium into a cell, against their concentration gradients Both (a) and (b) Which of these always involves the movement of a vesicle? diffusion facilitated diffusion endocytosis All of the above Which of the following occurs when a molecule fits into the binding site of a receptor protein on a cell’s surface? The receptor can open an ion channel in the cell membrane The receptor can act as an enzyme, causing chemical changes in the cytoplasm. The receptor can cause the formation of a second messenger. All of the above Which type of membrane protein transmits information into the cell by responding to signal molecules? receptor protein channel protei carrier protein glycoprotein What does a second messenger always do? sends a signal to another cel binds with a signal molecule from another cell activates an enzyme within a cell carries a signal within a cell