* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tunneling Effect and Its Applications Quantum
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot cellular automaton wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Erwin Schrödinger wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
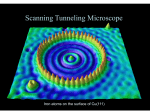
Quantum Mechanics: Tunneling Effect and Its Applications Discovery of Tunneling Effect Quantum mechanical tunneling works in the cold emission of electrons, semiconductor devices superconductor devices Applications: flash memory, RTD (resonance tunneling diodes) Scanning Tunneling Microscope The current leakage in MOSFETs (and Very-Large-Scale Integrated circuits, VLSIs) is due to tunneling through the supernarrow oxide barriers. It has been found that quantum tunneling may be the mechanism used by enzymes to speed up reactions in live cells to millions of times their normal speed Discovery of Tunneling Effect 1904-1968, George Gamow 1926-28 - PhD in St.Petersburg University 1928 - discovered beta-decay 1929-31 - in Bohr and Rutherford labs 1931-33 - Staff Fellow at Ioffe Institute 1932 - elected to the Academy of Sciences since 1934 - worked in U.S. predicted the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation 1948 - "The Origin of Chemical Elements" with Alpher (and Bethe) Gamow was a student of Alexander Friedman (1988-1925): in 1922 he found new solutions to the Einstein theory (general relativity field equations). Which is known nowadays as the expanding-universe solution. Discovery of Tunneling Effect 1928, George Gamow the theory of the alpha decay: decay of a nucleus via tunneling. Classically, the particle is confined to the nucleus because of the high energy requirement to escape the very strong potential. In quantum mechanics, however, there is a probability the particle can tunnel through the potential and escape. Then the half-life of the particle becomes finite and the energy of the emission is broadened. Ψ Max Born (1882-1970) Influenced by Gamow, Born developed a theory of quantum-mechanical tunneling. Modern Understanding of Tunneling Effect 1905, the photoelectric effect, Albert Einstein 1924, Louis de Broglie hypothesis Using relation between the wave length, wave vector, frequency etc we obtain that the energy and momentum in 1925 Schrödinger suggested wave function, the quantum phase or the probability wave Modern Understanding of Tunneling Effect in 1925 Schrödinger suggested wave function, we obtain that the energy the quantum phase or the probability wave and momentum If we take derivative of the phase we get ...or we get another derivative of the phase as ...which can be rewritten using the concepts of energy and momentum ...with the last step of making the second derivative... ... we arrive to the Schrödinger equation Modern Understanding of Tunneling Effect Solving 1D Schrödinger equation is almost trivial: Less trivial is the generalization to the case of the "negative" kinetic energy: the forbidden state Tunneling Through a Barrier For a classical particle the energy barrier is impenetrable: the particle coming from the left must be reflected Ar = Al A quantum particle, however, has a tail of the wave function under the barrier (non-zero probability) : then the particle coming from the left can be reflected OR transmitted Ar = Al + Br with the probability Discovery of Tunneling Diode the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physics Leo Esaki, Ivar Giaever "for their experimental discoveries regarding tunneling phenomena in semiconductors and superconductors, respectively" and Brian David Josephson for the Josephson effect Tunneling Diode: Principles Double Barrier Tunneling Diode