* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scanning Tunneling Microscope
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Super-resolution microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning joule expansion microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
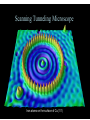
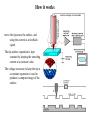
Scanning Tunneling Microscope Iron atoms on the surface of Cu(111) The scanning tunneling microscope was developed at IBM Zürich in 1981 by Gerd Binning and Heinrich Rohrer who shared the Nobel Prize for physics in 1986 because of the microscope. Heinrich Rohrer Gerd Binning d Metal tip Metal slab Inside the barrier the wave function dies off exponentially: So the probability of finding an electron after a barrier of width d is: And: Where I is the current through the closed circuit. Tunneling current is proportional to the distance between the tip and the surface. How it works move the tip across the surface, and using the current as a feedback signal. The tip-surface separation is kept constant by keeping the tunneling current at a constant value. The voltage necessary to keep the tip at a constant separation is used to produce a computer image of the surface.