* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the PDF file to learn more
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
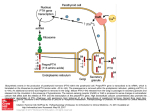
BioSens-All™: A New Technology Dedicated to GPCR Biased Ligand Drug Discovery Billy Breton,1 Nathalie Rouleau,1 Mélanie Frauli,2 and Stephan Schann2 1. Domain Therapeutics NA Inc, NeoMed Institute, 7171 Frederick Banting, Montréal Québec H4S 1Z9, Canada. 2. Domain Therapeutics, Blvd Sébastien Brant, 67400 Strasbourg-Illkirch, FRANCE. [email protected] INTRODUCTION GPCRs have proven to be a valuable target family for drug discovery and development with more than 30% of marketed drugs acting through this receptor superfamily. However, numerous GPCR members remain challenging with no selective and druggable ligands being successfully developed. For these difficult targets, novel strategies consisting in developing allosteric modulators and biased ligands (BLs) are now emerging. Indeed, all GPCR agonists do not always uniformly activate all signalling pathways mediated by a given receptor. BLs therefore constitute a novel approach to more selectively activate a receptor for the development of safer drugs. This concept of ligand bias, also referred to as functional selectivity, has now been validated in vitro and in vivo, and several GPCR BLs are currently under clinical investigations. Despite these promising features, uncovering and profiling BLs still remains challenging as no specific technology has been proposed for this task. Cell-system dependency of the multiple functional analyses for instance makes it difficult to guide medicinal chemists in their optimization programs toward active BLs. To meet this expectation, the dedicated BioSens-All™ technology was generated. BioSens-All™ consists in a set of multiple biosensors each engineered to follow one specific functional pathway. The parallel characterization of GPCR orthosteric or allosteric ligands with theses biosensors, in a homogenous format, enables the generation of signalling signatures and consistent comparative data for chemists. The present poster will present and exemplified how BioSens-All™ can be used to support medicinal chemists in their quest for GPCR biased ligands. 1. Biased Ligands: The Theory • 2. A fully Integrated Platform to Identify Biased Ligand GPCRs constitute complex receptors that can engage multiple signaling pathways upon Specific binder selection using a FRET-based binding assay: DTect-All™ • activation (a). Use as a filter to focus only on binders of the GPCR • Therapeutic efficacy is often driven by a single pathway, adverse events by others. • Biased ligands selectively activate one pathway given rise to safer drug candidates (b). This is Wide functional profiling with multiple BRET-based biosensors: BioSens-All™ • Enable clustering of binders based on their signalling signatures done by stabilization of specific receptor conformation. Biased clusters assessed using native assays for efficacy and side effect profile • Deliver fully validated biased hits / leads Small molecules, peptides or antibodies Validated hits for ready for optimization Galandrin S et al, TiPS 2007 3. Domain’s New Technology: BioSens-All™ • Native systems characterization BRET-based biosensors each designed to follow activation of one functional pathway Cluster #1 • Profiling of multiple signaling pathways done in parallel in a same cellular background Cluster #2 Cluster #3 … • Simple transfection of non-modified GPCR with intracellular BRET signal • Profiling in homogenous assay format enabling direct comparison for biased ligand characterization • Determination of signaling signature of each GPCR binder Wide functional profiling FRET • • • • • • • • • • Gs Gi1/2/3 GoA/B Gq Gz G11 G12 G13 G14 G15/16 GFP GFP • • • • • b-arrestin-1 b-arrestin-2 • • • • • • • Ca2+ cAMP DAG Dye TPR1 GRK2/3 PKC p63 Merlin p115 Internalization C-ter domain C-ter domain C-ter domain Step 1 PROXIMAL Step 2 • Was shown to activate alternative pathways such as Gq/Ca2+/PKC, beta-arrestin 2 100 90 80 E C 5 0 = 5 6 .9 p M PTH % o f n o n s tim u la t e d Class B GPCR activating the canonical Gs/cAMP/PKA pathway 100 T y r1 -P T H 80 60 -1 6 -1 4 -1 2 -1 0 -8 -6 -4 -1 6 lo g [ P e p t id e ] ( M ) [Tyr1]PTH(1-34) 0,6nM (100%) 0,7nM (100%) 0,01nM (full) 0,06nM (full) 0,06nM (full) 3nM (full) 95 P T H E C 5 0 = 3 5 .1 n M T y r 1 -P T H -1 4 -1 2 Beta-arrestin 1,3nM (100%) 27nM (56%) Internalization 5nM (100%) 104nM (75%) -6 -4 E C 50= 16 2 nM B-arrestin recruitment biosensor PTH + PTX T y r 1 -P T H 150 100 -1 0 -8 -6 -1 6 -4 -1 4 -1 2 -1 0 -8 -6 -4 lo g [ P e p t id e ] ( M ) b a r r 2 b io s e n s o r > 10µM 13,4nM > 10µM 1,1nM (full) 34,2nM (partial) 2 90 80 P T H E C 5 0 = 1 3 .4 n M -1 6 -1 4 -1 2 PTH E C 5 0 = 1 .1 n M T y r 1 -P T H E C 5 0 = 3 4 .2 n M 300 200 100 T y r 1 -P T H 70 % o f n o n s t i m u la t e d 162nM (full) 100 BRET > 10µM 2 400 % o f n o n s t i m u la t e d Go PTH lo g [ P e p t id e ] ( M ) > 10µM > 10µM % o f n o n s t i m u la t e d 2 100 G o b io s e n s o r 35,1nM 16nM (100%) -8 90 BRET 30nM (100%) -1 0 E R K -N L S 1 5 m in BRET 2 PTH(1-34) Gq ERK 1/2 BRET [Tyr1]PTH(1-34) Gs IP1 BioSens-All™ PTH(1-34) -1 2 200 % o f n o n s t i m u la t e d Cupp ME et al, JPET 2013 -1 4 lo g [ P e p tid e ] (M ) G q b io s e n s o r profiled with BioSens-All™ compared with the endogenous PTH(1-34) E C 5 0 = 5 5 .4 p M T y r 1 -P T H E C 5 0 = 3 0 0 0 p M 70 Numerous BLs were already described for PTH1R: [Tyr1]PTH(1-34) was chosen and G-protein activation biosensors P T H E C 5 0 = 9 .7 p M recruitment or ERK(1/2) phosphorylation cAMP Step 3 c A M P b io s e n s o r BRET PTH1 receptor (PTH1R) plays key role in bone remodeling % o f n o n s t i m u la t e d BRET 2 G s b io s e n s o r • • C-ter domain DISTAL 4. Illustrative example • GFP Dye -1 0 -8 lo g [ P e p t id e ] ( M ) -6 -4 -1 6 -1 4 -1 2 -1 0 -8 -6 -4 Same level of potency and similar bias as that described in the literature was found using BioSens-All™ technology lo g [ P e p t id e ] ( M ) Conclusion Biased ligands represent a novel research strategy for the development of safer drug candidates targeting GPCRs. This class of agonists / PAMs / antagonists or NAMs are specifically activating / potentiating / blocking only one or a fewer signaling pathway(s) of the receptor. A new technology called BioSens-All™ was specifically designed for their identification and characterization. BRET-based BioSens-All™ can be used as a stand alone tool or in a fully integrated manner in combination with the FRET-based DTect-All™ binding assay.