* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CISCO Secure Intrusion Detection System
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Denial-of-service attack wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
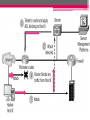
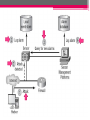
CISCO Secure Intrusion Detection System Marsa Rayani Maryam Shahpasand Ali Falsafi Contents: • • • • • • • • • • • Introduction CSIDS definition CSIDS components CSIDS features CSIDS Platforms Cisco Security Agent Advantages Disadvantages CSIDS VS. Snort Summery references Introduction: Cisco security experts believe that The most effective intrusion detection strategy is to implement both host-based and network-based IDS. Typically, most organizations implement network-based IDS first, because it’s effective against attacks originating externally. Adding host-based IDS further enhances protection from attack, especially from attacks that are generated from internal sources. To achieve these elements, Cisco implements a line of IDS products that can be integrated into • • • • current network routers switches deployed as separate IDS appliances run as software applications on management workstations. • Cisco Secure IDS is a network-based intrusion detection system that uses a signature database to trigger intrusion alarms Components: The major components are: 1. 2. 3. 4. Sensor Configuration Manager Event Manager Software Components : 1. Sensor : This performs real-time monitoring of network traffic, searching for patterns that could represent an attack. Performance of the Sensor when it detects an attack: No action Shun (shunning) refers to the complete blocking of any traffic from the offending host or subnet Log (logging) refers to both attack event alarms and whole suspicious IP session logs Shun + log TCP connection reset TCP connection reset + shun TCP connection reset + log TCP connection reset + shun + log 2. Configuration manager : The configuration manager provides configuration management for the sensor pushing configuration and policy settings to the sensor. The configuration manager may be co-located with the sensor (typical for smaller sensor deployments) or may be separately located at a central location (typical for larger sensor deployments). 3. Event manager : The event manager is used to collect events generated by sensors. Cisco Secure IDS event management platforms include a Network Security Database (NSDB), which includes detailed information about each attack that is detected by a sensor. This information provides analysis support for security administrators who must decipher and respond to detected attacks. Cisco Secure IDS sensors have extremely limited event management capabilities; hence the event manager is always separate from the sensor. 4. Software: Cisco Secure IDS (CSIDS) isn’t just a set of hardware components—it also includes software that has evolved over years. Communication between Sensor and management platform: To communicate messages between the management platform and the sensor platform, Cisco Secure IDS uses a proprietary protocol called the PostOffice protocol. This protocol provides numerous necessary features, such as the following: • Reliability • Redundancy • Fault tolerance Reliability 1 2 Redundancy Fault Tolerance Cisco Secure IDS Features Cisco offers a rich IDS product set that is part of Cisco’s SAFE enterprise security blueprint. Cisco Secure IDS has many features that let you effectively detect and respond to security threats against your network. It provides the following fundamental capabilities: 1. Alarm display and logging 2. Intrusion response 3. Remote sensor configuration and management These features are discussed in the following sections. 1. Alarm Display and Logging When a sensor detects an attack, it sends an alarm to the event management platform. On the event management platform, a graphical user interface (GUI) displays these alarms in real time, color-coding each alarm based on its severity. This display provides a quick indication that an attack has occurred and how dangerous the attack is. The sensor can also log more detailed alarm information in a local text-based log file, which allows for in-depth analysis of attack data and the use of custom scripts to present alarm data specific to your requirements. 2. Intrusion Response The Cisco Secure IDS sensor can directly respond to an attack using one or more of the following methods: I. TCP reset II. IP blocking III. IP logging I. TCP reset: The TCP reset response is available only for TCPbased attacks. It’s implemented by the sensor sending a TCP reset packet to the host that is being attacked (the target). This causes the attacked system to close the connection, destroying any processes and memory associated with the connection. II. IP blocking The IP blocking response (also known as shunning) allows a sensor to apply an access control list (ACL) to a perimeter router interface, blocking IP connectivity from an attacking system. You can also manually block a host or network from the sensor management platform if you see any suspicious activity III. IP logging When a sensor detects an attack, an alarm is generated and forwarded to the event management platform. The IP logging response allows a sensor to write alarm information to a local log file as well. The information written to the log file contains much more information than is sent to the event management platform, so you can use this option to provide detailed analysis of specific attacks. 3. Remote Sensor Configuration and Management • Cisco Secure IDS sensor management platforms let you centrally manage and monitor multiple sensors located throughout your network. • All sensor-related configurations are stored on a configuration management platform. • configuration management platform is responsible for pushing these configurations out to each sensor. • Configuration attributes include the types of intrusive activity (signatures) that each sensor should monitor. Other Features Cisco Secure IDS also includes • an Active Updates feature, which allows customers to subscribe to regular e-mail notifications generated by the Cisco Countermeasures Research Team (C-CRT). • download new signature updates to a central location on the network, and then have multiple sensors automatically update their signature databases on a regular basis. • Customize signatures: you create your own signatures that can detect some new attack. This functionality is provided by a complete signature language, which is similar to a scripting language, providing a powerful tool for customization. Cisco Secure Sensor Platforms • The sensor platform is the most critical component of Cisco Secure IDS, because it detects, responds to, and reports intrusion activity to the sensor management platform. • Each sensor is a hardware appliance that has been secured for the environment it works in, optimized for performance, and designed for ease of maintenance. • The sensor uses an extensive signature database that allows it to capture security attacks in realtime from large amounts of IP traffic. • Sensor possesses packet-reassembly features that prevent IDS bypass techniques. • Once an attack is detected, the sensor sends an alarm to an event management platform and can optionally place that alarm information in a local log file. • The sensor can also automatically reset a TCPbased connection that is associated with the attack and/or block the source IP address of the attacking system. Cisco produces three main sensor platforms dedicated to IDS: • 4200 series sensors • Catalyst 6000/6500 IDS module (IDSM) • Cisco 2600/3600/3700 IDS network modules Sensors Interface All of these sensor platforms are passive sensors, in that they passively monitor network traffic traversing one or more segments for intrusive activity. Each of these sensors contains two interfaces: I. Command-and-control interface II.Monitoring interface I. Command-and-control interface • provides a management interface for the sensor. • The command-and-control interface allows the sensor to be managed via TCP/IP. • lets the sensor send alarms to the event management platform. • The command-and-control interface is the only interface that contains an IP address. II. Monitoring interface • The monitoring interface operates in promiscuous mode, capturing all traffic on the attached segment and passing it to the IDS application for analysis. • The monitoring interface doesn’t have an IP address. • ensuring that the sensor can be placed on an insecure segment and not be subjected to an attack itself Cisco Security Agent • The Cisco Security Agent consists of server and desktop agents. • The security agent resides between the operating system kernel and applications. • enabling visibility of all system calls to memory, file, network, Registry, and COM object resources. • Cisco Security Agent is an example of an anomalybased intrusion detection system. • It is useful for detecting new attacks that are often impossible to detect with signature-based intrusion detection systems such as Cisco Secure IDS sensors • The Cisco Security Agent provides a variety of features that ensure that critical systems and applications are protected from attacks. It’s designed to detect known and unknown attacks based on the following intrusive activities: I. Probing II. Penetration III.Persistence IV.Propagation V. Paralyzing I. Probing Probing relates to the activities associated with reconnaissance being performed against the host or an attempt to break into a host by guessing security information. The following are some of the probe attacks that the Cisco Security Agent detects: Ping Port scans Password and username guessing II. Penetration Penetration refers to the process of gaining unauthorized access to processes running and/or data stored on the target system. The Cisco Security Agent can detect a possible attack based on events that indicate the host is in the process of being compromised or penetrated. The following are some of the events related to penetration attacks that the Cisco Security Agent detects: Mail attachments Buffer overflows ActiveX controls Back doors III. Persistence Persistence refers to events that result from a successful attack and subsequent infection of a host system. The following are some of the events that indicate that a system has been compromised and that some form of unauthorized action, application, or service is present: File creation File modification Security settings modification Installation of new services Trap doors IV. Propagation Propagation refers to the automatic selfreplication of an attack to other systems after an initial target system has been infected. There are some of the events related to propagation that the Cisco Security Agent detects: E-mail copies of the attack Web and FTP connections Internet Relay Chat (IRC) connections Propagation via file shares V. Paralyzing Paralyzing refers to the complete or partial removal of the availability and responsiveness of computing resources on a target system. The following are some of the events related to system paralysis that the Cisco Security Agent detects: File modification and deletion Computer crashes Denial of service Stealing of sensitive/confidential information Advantages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Accurate attack detection Intelligent attack investigation Ease of security management Flexible deployment options for all network design models and topologies 5. you can create your own signatures that can detect some new attack. Cont. 6. combines leading Cisco security solutions with a rich ecosystem of complementary programs, products, partners and services. 7. Focuses on large businesses 8. Assumes a security policy Disadvantaged • Expensive • Black box design, you’ll have no idea why it does anything that it does. • Closed signature language, you have no ability to see what or how they’re trying to detect anything. • Difficult to install. • Difficult to administer CSIDS VS Snort Battle of Open Source VS Commercial! • Snort has a better GUI. • Snort biggest advantage is COST. • CSIDS is better at both IP fragment and TCP session reassembly. • CSIDS has an excellent support and services. • For small environments where funds are very limited, snort is probably the better solution. • For large enterprises, Cisco would probably be the better choice. References • • • • • www.cisco.com CCSP Complete study book by Cisco www.net-security.org/ www.ciscopress.com/articles https://itaudit.sans.org/community/papers/aud iting-cisco-secure-ids-system-auditorsperspective_114