* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 - River Mill Academy
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
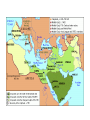
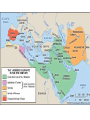
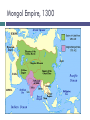
UNIT 4 Day 32: Islam Quiz 8! 1. The ______ built their capital Tenochtitlan on a swamp and grew crops in floating gardens. 2. The ______ built the first city in North America called Cahokia. 3. Quipu were strings with knots tied to keep records, used by the _____. 4. Which leader created the 1st unified Chinese empire in the Qin Dynasty, and used legalism to keep order in society? 5. What had to be studied in order to pass the Han civil service exam? 6. What is a dowry? 7. Name one explorer allowed into the Yuan Dynasty court during Kublai Khan’s reign. 8. Which empire closed off China to the rest of the world in 1435? 9. What is the name for ancient Indian writing? 10. What three groups are the “People of the Book?” Quiz Answers! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Aztecs Mississippians Incas Shi Huangdi Confucian Classics/Literature/Philosophy/writing Money paid to man for marrying woman Marco Polo, Ibn Battuta Ming Sanskrit Muslims, Jews, Christians Early Growth of Islam Muhammad dies, next leader of Islam? Abu Bakr (M’s father in law)1st caliph Caliph=successor to Muhammad Arabs not as loyal as they were to Muhammad Once Arabs unite, conquer Byzantine and Persian empires (neighbors) Capture Syria and Palestine, Damascus and Jerusalem, Egypt Division Sunni Believed any good Muslim could lead the community There can be no Prophet after Muhammad What defines a “good” Muslim?? Fight! Inspiration comes from Muhammad’s example Shiite (Shia) Believed Muhammad chose son-in-law Ali to be successor True successors are descendants of Ali and Fatima Called Imams (divinely inspired leaders) Compare Sufis Muslim mystics, seek communion with God through meditation, fasting, rituals; pious, miraculous power? Help spread Islam by traveling, preaching, examples Sunni Both Shiite Umayyad Caliphate, until 750 Rule after death of Ali, dynasty of Sunnis Capital at Damascus (Syria) Battle of Tours: defeated by Franks (France) Rule parts of Spain but no expansion into Europe Success of Um Caliphate due to: 1. Weakness of Byz and Pers. Empires 2. Arab bold/efficient fighting methods 3. Common faith, religion Fair treatment of conquered people Keep religion, pay tax or convert and gain equality Abbasid Dynasty, 750-1258 Leader: Abu al-Abbas (descend from M’s uncle) Supported by Shiite & non-Arab Muslims Empire based on equality of all Muslims Empire of caliphs reaches greatest wealth and power Islam becomes more diverse, discrimination of non-Arab Muslims ends Vizier: head of bureaucracy, most imp gov’t official Capital: Baghdad Minarets: slender towers of the mosques Decline of Muslim Empire Seljuk Turks: migrate to Middle East Adopt Islam, build empire 1055, Seljuk sultan *ruler* controlled Baghdad Abbasid caliph = figurehead Mongols, 1258 Hulagu (grandson of Ghengis) sacks Baghdad Killed last Abbasid caliph Adopt Islam Late 1300’s, Mongol Leader Tamerlane (Muslim) Mongol Empire, 1300 Social/Economic Advances Trade network using camels (ships of the desert) Sahara to W. Africa Silk Road Indian # system, banks, checks Agriculture, irrigation projects Herding, farming Muslims have social mobility Can improve social rank through religion, school, military Slaves were household servants Art/Literature Muslim leaders forbid painting God or humans in religious art Poetry, storytelling, The Thousand and One Nights Calligraphy (art of beautiful handwriting) Knowledge Translated Persian, Sanskrit, Greek into Arabic Philosophy Math (standardized textbook), astronomical tables Hospitals, studies measles, smallpox Way to treat cataracts, diseases, etc.