* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Structure
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
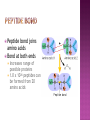
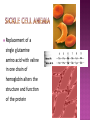
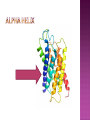
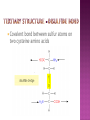
From: Protein Data Bank PDB ID: 1B0E Kalus, W., Zweckstetter, M., Renner, C., Sanchez, Y., Georgescu, J., Grol, M., Demuth, D., Schumacher, R., Dony, C., Lang, K., Holak, T. A.: structure of the IGF-binding domain of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5): implications for IGF and IGF-I receptor interactions. EMBO J 17 Diverse functions related to structure Structural components of cells Motor proteins Enzymes Antibodies Hormones Hemoglobin/myoglobin Transport proteins in blood Amino acids Amino group (NH2) Carboxyl group (COOH) 20 amino acids make up protein 8 essential amino acids (must be eaten in diet) 9 in infant (histidine) 5 bonds or forces determine structure Peptide bond Hydrogen bond Disulfide bond Ionic bond Hydrophobic force Peptide bond joins amino acids Bond at both ends Increases range of possible proteins 1.0 x 1026 peptides can be formed from 20 amino acids Linear sequence of amino acids forms primary structure (long chain of amino acids) Sequence essential for proper physiological function Replacement of a single glutamine amino acid with valine in one chain of hemoglobin alters the structure and function of the protein Peptide chains fold into secondary structures to become more compact: - helix - pleated sheet Secondary structures fold and pack together to form tertiary structure Usually globular shape Tertiary structure stabilized by bonds between R groups (i.e. sidechains) All amino acids contain a carboxyl group and an amino group. R-Groups distinguish between individual amino acids. R-Groups make them different from one another. Hydrogen bonds are weak electrical attractions between positively and negatively charged atoms of different molecules. Covalent bond between sulfur atoms on two cysteine amino acids Ions on R groups form bridges through ionic bonds Ionic bonds form from the exchange of electrons between atoms Example: NaCl (table salt) Close attraction of non-polar R groups in the chains Very weak but collective interactions over large areas help stabilize the protein structure The arrangement of many tertiary structures into one large protein molecule Not all proteins have or need a quaternary structure Allows for changes in structure/function in response to chemical stimuli