* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microbiology ELISA questions
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
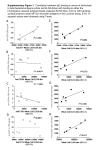
Shaylyn Robison ELISA Questions Micro Lab BIOL 2065 W 10 am-11:50 am ELISA Questions 1.) ELISA stands for Enzyme-Link Immunosorbent Assay. It is a test that uses a catalyzed color reaction to detect antigens or antibodies. There are two types of ELISA: Direct or Indirect. Direct ELISA is used in testing for virus particles from samples. It tests for toxins and pregnancies. The Indirect ELISA detects antibodies such as anti-HIV antibodies in AIDS testing and other important clinical testing. The ELISA test is sensitive because you use specific antibodies that are specific to certain antigens. It is necessary to block unoccupied binding sites in the wells so that antigens do not bind to the walls of the wells. The positive control is the primary antibody and it is important to have a control because so that you know if the results yielded are correct. The control well contains viral antigens and the anti-IgG peroxidase conjugate; it should not change color during the experiment. 2.) It takes several years for a person to show the symptoms of AIDS because first the person must be infected by HIV. HIV degrades the immune system slowly and the person then becomes susceptible to other diseases after their immune system becomes damaged. AIDS is the combination and culmination of rare diseases and cancers that people develop who are infected with HIV. 3.) Anti-HIV-1 IgG is screened instead of the virus itself so that the ELISA is able to detect the antibodies because it is such a sensitive test. The ELISA is designed to be easy to perform and inexpensive, and is used as a first, initial test for HIV. Detecting the virus directly is deemed “impractical” which is why the antibody is used in the ELISA test. 4.) T helper cells are the first cells to detect a foreign substance and will alert B cells and an immune response. By destroying T cells, HIV eliminates the body’s ability to mount a counter offense because the T cells cannot alert B cells nor help in the coordinated immune system response. HIV attaches itself to the T cell and injects its RNA into the cell, which then becomes a host cell. This process renders the T cell useless and therefore weakens the immune system. 5.) There are so many variants of HIV because of mutation and reverse transcriptase (the enzyme that does the replication process) does not proofread it’s work. 6.) To make the primary antibody into an enzyme conjugate would make the ELISA test more sensitivity and not as specific. Proteins that may cross-react with antibodies or the enzyme and bind to the antibody-conjugate in the ELISA test could create a false positive.