* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Targets for dopaminergic ligands
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition and cognition wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
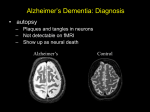
Synaptic Function 1: Dopamine Targets for dopaminergic ligands Tyrosine Dopamine synthesis L-DOPA DA Glial cell Vesicles Pre-synaptic terminal Dopamine Transporters MAO-B COMT D2 Receptors Post-synaptic cell Targets for dopaminergic ligands Tyrosine L-DOPA F18-Dopa DA Glial cell Vesicles Pre-synaptic terminal MAO-B COMT I123 IBZM or epidepride I123 FPCIT or ß-CIT Post-synaptic cell *** Dopamine transporter imaging Normal Dopamine Transporter (DATSCAN) images Head of Caudate MRI Putamen DATSCAN SPECT Body of Caudate A PD image with DaTSCAN Medial part of SN projects to caudate Lateral part of SN projects to putamen In PD the lateral part of SN always degenerates first preferential loss in putamen relative to caudate Diagnosis and staging of Parkinson’s Disease Clinical diagnosis Imaging diagnosis Accuracy of Diagnosis in Presumed PD Meara J et al Age and Ageing 1999;28:99-102 . •26% of patients receiving inappropriate treatment Post-mortem data suggests figure may even be higher Even on first presentation SPECT shows loss of 50% of neurones Objective measurement of progression in assessment of therapy Normal PD: H&Y1 PD: H&Y2 PD: H&Y3 Can we show progression in an individual patient? 51 year old lady, first Presentation Caudate Putamen 18 months 36 months ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– R L R L R L 4.29 3.84 4.14 3.14 3.31 2.40 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2.05 1.32 1.56 1.17 1.17 1.07 ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– Specific/Non-specific ratios 2: Serotonin Serotonin Transporter [SERT] imaging Clinical depression Major Depression • • prevalence as high as 10% key symptoms low mood diminished interest in pleasure hopelessness, guilt, suicidality cognitive impairment changes in sleep, appetite, libido • World Bank report - global burden second only to IHD by 2020 Treatment of depression The Monoamine Hypothesis • 1950s - drugs used to treat TB and schizophrenia were found to elevate mood and stimulate activity • First tricyclic antidepressant - found to increase the activity of the monoamine neurotransmitters by inhibiting their reuptake • Thus, antidepressants appeared to work by normalising a deficit in monoamines, especially serotonin • Drugs highly selective for the serotonin system were developed Action of SSRI antidepressants Pre-synaptic terminal Serotonin transporters (SERT) Synapse Serotonin Serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) 123I-beta-CIT Post-synaptic cell Image available binding sites Analysis of 123I-beta-CIT scans for SERT availability SPECT scans at 3 hours reflect SERT binding in midbrain regions These are sagittal views through the midline in 2 patients High drug effect on transporters Lower drug effect on transporters Availability is a measure of the number of transporters available to transport neurotransmitter [serotonin] from the synapse back into the pre-synaptic terminal. SERT availability = (MB - OCC)/ OCC where MB and O CC are tracer count rates in the mid-brain and in the occipital reference region. Analysis of 123I-beta-CIT scans for DAT availability SPECT scans at 24 hours reflect DAT binding in the striatum This is an axial view through the basal ganglia. DAT availability = (ST - OCC)/ OCC where ST and O CC are tracer count rates in the striatum and in the occipital reference region. SERT availability for patients on SSRIs or venlafaxine 1.00 0.80 The normal availability index is around 2.7 0.60 SERT Availability 0.40 0.20 0.00 Non-responders Responders •9 out of 11 patients in the SSRI or SNRI groups with binding indices between 0.2 and 0.6 were responders and all 7 outside this range were non-responders •This suggests that response could be improved by better regulation of the degree of transporter downregulation - See also( Meyer et al, Amer J Psych 2004) DAT binding indices for patients on antidepressants as a function of age 12.00 10.00 8.00 DAT 6.00 Availability 4.00 2.00 0.00 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Age •This is consistent with the literature and indicates a decline of 7.3% per decade. Dementia: the diagnostic dilemma • Alzheimer's disease • Dementia with Lewy bodies • Frontal lobe dementia, including Pick's disease • Alcohol related dementia • Vascular dementia [email protected] Therapy for AD Cholinergic projections The acetylcholine neurotransmitter system is selectively affected in AD Therapies aim to improve cholinergic neurotransmission Septum Basal nucleus MR in psychiatry • Alzheimer’s disease - progression Normal ageing Early onset AD difference at 12m difference at 12m Alzheimer’s disease - progression A typical SPECT perfusion scan The AD perfusion pattern • The probability that patients with memory loss and normal perfusion had Alzheimer's disease was 19 %. • The probability of Alzheimer's disease with bilateral temporoparietal defects was 82% Alzheimer's disease progression • 57 year old man presenting with gradually deteriorating memory Initial 99mTcHMPAO SPECT Follow-up at 4.5 years Frontal lobe dementia • Frontal hypo-perfusion sometimes including temporal lobes Alzheimer’s disease Bi-lateral temporo-parietal deficits Frontal lobe dementia Bi-lateral frontal lobe deficits Vascular dementia • Multiple regions of focally reduced perfusion Early diagnosis? Ann Neurol 2004;55:306-319