* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RF Fundamentals
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
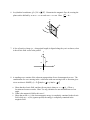
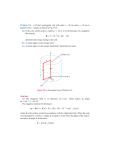
RF Fundamentals FINAL EXAM Due December 11 12:00 noon Each problem is worth 0 points. 1. A sphere of radius 2 cm contains a volume charge density given by 4 cos 2 (C / m 3 ) Find the total charge Q contained in the sphere. Hint: d cos sin . d 2. Three point charges, each with q = 3 nC, are located at the corners of a triangle in the x-y plane, with one corner at the origin, another at (2 cm, 0, 0), and the third at (0, 2 cm, 0). Find the force acting on the charge located at the origin. 3. In a given region of space, the vector magnetic potential is given by A xˆ 5 cos y zˆ 2 sin x Wb . m a. Determine β . b. Use A dsˆ Wb to calculate the magnetic flux passing through a square loop with 0.25-m-long edges if the loop is in the x-y plane, its center is at the origin, and its edges are parallel to the x- and y-axes. 4. The electromagnetic generator shown in Fig. 6-12 is connected to an electric light bulb with a resistance of 100 . If the loop area is 0.1 m2 and it rotates at 3600 revolutions per minute in a uniform magnetic flux density, o 0.2 T , determine the amplitude of the current generated in the light bulb. m in spherical coordinates, find the current crossing the spherical 5. Given J 10 3 sin rˆ A 2 shell, r 0.02 m . Hint: sin 2 1 cos 2 . 2 6. In cylindrical coordinates, β 2.0 / r ˆ T . Determine the magnetic flux, , crossing the dr ln r . plane surface defined by 0.5m r 2.5m and 0m z 2.0m. Hint: r z 2.0 dŝ 0 0.5 2.5 7. A line of positive charge (L = charge/unit length) is aligned along the y-axis as shown, what is the electric field vector at the point P. y P a +L x -L 8. A standing wave consists of the coherent superposition of two electromagnetic waves. The combination of a wave moving in the +x direction with one moving in the -x direction gives rise to an electric field Ex, t Em y sin( kx t ) y sin( kx t ). a. Show that the electric field vanishes (for any time) whenever x n / k . (These x locations are known as nodes. Hint: Use trig. identities for sum and differences of an angle. b. What is the magnetic field for this wave? c. Show that at time t = 0, the electromagnetic energy is completely contained in the electric field, while at t = (quarter period) the energy is completely contained in the magnetic field. 9. What are the Maxwell equations, and how do they differ between electrostatics, magnetostatics, and electrodynamics? 10. A square loop is coplanar with a long, straight wire carrying current i(t ) 2.5 cos 2 10 4 t ( A) a. Determine the emf induced across a small gap created in the loop. b. Determine the direction and magnitude of the current that would flow through a 4- resistor connected across the gap. The loop has an internal resistance of 1-. z For a long wire carrying current, recall that: 10 cm 10 cm i(t) l x I β φˆ o 2r 5 cm y