* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 16.Abnormal PsychologyDSM5
Selective mutism wikipedia , lookup
Kleptomania wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Gender dysphoria wikipedia , lookup
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
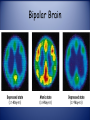
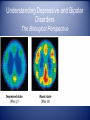
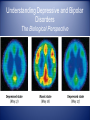
Abnormal Psychology A “harmful dysfunction” in which behavior is judged to be disturbing, atypical, maladaptive and unjustifiable. Historical Perspective Perceived Causes movements of sun or moon lunacy--full moon evil spirits Ancient Treatments exorcism, caged like animals, beaten, burned, castrated, mutilated, blood replaced with animal’s blood Early Theories • Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out. • Trephining was often used. Early Theories •trephening: Cutting a hole in the head of the afflicted to let out the evil spirit. Early Theories • Another theory was to make the body extremely uncomfortable Philippe Pinel early hospitals • French doctor who was the first to take the chains off and declare that these people are sick and “a cure must be found!!!” History of Mental Disorders • In the 1800’s, disturbed people were no longer thought of as madmen, but as mentally ill. They were first put in hospitals. Did this mean better treatment? Early Mental Hospitals • They were nothing more than barbaric prisons. •The patients were chained and locked away. •Some hospitals even charged admission for the public to see the “crazies”, just like a zoo. DSM-5 http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/classification-and-diagnosis.html • Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the big book of disorders. • DSM will classify disorders and describe the symptoms. • DSM will NOT explain the causes or possible cures. Acknowledgement A significant number of Wikipedia articles were used in the development of this PowerPoint presentation and are not always appropriately cited due to space constraints. Neurodevelopmental Disorders • Intellectual Disability (IQ and Adaptive Functioning) • Communication Disorders (ex. Speech Sound Disorder) • Autism Spectrum Disorder (characterized by social deficits, communication difficulties, stereotyped or repetitive behaviors and interests, and in some cases, cognitive delays) • Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (incl. combined, inattentive and hyperactive/compulsive) • Specific Learning Disorder (incl. reading, writing, and math) • Motor Disorders • Tic Disorders (ex. Tourette’s Disorder) • Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders • • • • • Schizotypal (Personality) Disorder (characterized by a need for social isolation, anxiety in social situations, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs) Delusional Disorder (characterized by non-bizarre delusions, but with no accompanying prominent hallucinations, thought disorder, mood disorder, or significant flattening of affect) Brief Psychotic Disorder Scizophreniform Disorder: being similar to schizophrenia in appearance or manifestations but tending to last usually more than two weeks and less than six months Schizophrenia: a psychotic disorder characterized by loss of contact with the environment, by noticeable deterioration in the level of functioning in everyday life, and by disintegration of personality expressed as disorder of feeling, thought (as in delusions), perception (as in hallucinations), and behavior Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders (Cont.) • • • • • • • • Schizoaffective Disorder: relating to, characterized by, or exhibiting symptoms of both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (Bipolar and Depressed Types) Substance/Medication Induced Psychotic Disorder Psychotic Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition (with delusions; with hallucinations) Catatonia Assoc. With Another Mental Disorder Catatonic Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition Unspecified Catatonia Other Specified Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorder Unspecified Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorder Bipolar and Related Disorders • • • • • • • Bipolar I Disorder (characterized by at least one manic or mixed episode) Bipolar II Disorder (characterized by at least one episode of hypomania and at least one episode of major depression) Cyclothymic Disorder (characterized by numerous extreme mood disturbances, with periods of hypomanic symptoms alternating with periods of mild or moderate depression) Substance/Medication Induced Bipolar and Related Disorder Bipolar and Related Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition Other Specified Bipolar and Related Disorder Unspecified Bipolar and Related Disorder Depressive Disorders Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder Major Depressive Disorder Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia) Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder Substance/Medication-Induced Depressive Disorder Depressive Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition • Other Specified Depressive Disorder • Unspecified Depressive Disorder • • • • • • Anxiety Disorders • • • • • • • • • • • • Separation Anxiety Disorder Selective Mutism Specific Phobia Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia) Panic Disorder Panic Attack Specifier Agoraphobia (characterized by anxiety in situations where the sufferer perceives certain environments as dangerous or uncomfortable, often due to the environment's vast openness or crowdedness) Generalized Anxiety Disorder Substance/Medication-Induced Anxiety Disorder Anxiety Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition Other Specified Anxiety Disorder Unspecified Anxiety Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders • • • • • • • • • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (characterized by intrusive thoughts that produce uneasiness, apprehension, fear, or worry; by repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing the associated anxiety; or by a combination of such obsessions and compulsions) Body Dysmorphic Disorder (characterized by concern with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect regarding physical features) Hoarding Disorder Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder) Excoriation (Skin-Picking) Disorder Substance/Medication-Induced Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition Other Specified Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorder Unspecified Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorder Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders • • • • • • • Reactive Attachment Disorder (characterized by markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate ways of relating socially in most contexts. It can take the form of a persistent failure to initiate or respond to most social interactions in a developmentally appropriate way—known as the "inhibited form"—or can present itself as indiscriminate sociability, such as excessive familiarity with relative strangers—known as the "disinhibited form“ – see below) Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (Includes PTSD for children 6 years and younger) Acute Stress Disorder Adjustment Disorders Other Specified Trauma and Stressor Related Disorders Unspecified Trauma and Stressor Related Disorders Dissociative Disorders • Disruption in the usually integrated functions of consciousness, identity, memory or perception of the environment • Dissociative Identity Disorder (a.k.a. Multiple Personalities Disorder) • Dissociative Amnesia (specify if with dissociative fugue - loss of memory sometimes including the memory of personal identity due to brain injury, shock, fatigue, repression, or illness) • Depersonalization/Derealization Disorder • Other Specifies Dissociative Disorder • Unspecified Dissociative Disorder Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders • • • • • • • Somatic Symptom Disorder (any of a group of psychological disorders marked by physical complaints for which no organic or physiological explanation is found and for which there is a strong likelihood that psychological factors are involved) Illness Anxiety Disorder (formerly Hypochondriasis) Conversion Disorder causes patients to suffer from neurological symptoms, such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits without a definable organic cause. It is thought that symptoms arise in response to stressful situations affecting a patient's mental health. Psychological Factors Affecting Other Medical Conditions Factitious Disorder (Intentionally produced physical or psychological symptoms: Includes FD imposed on self or another) Other Specified Somatic Symptom and Related Disorder Unspecified Somatic Symptom and Related Disorder Feeding and Eating Disorders • • • • • • • • Pica (characterized by an appetite for substances largely non-nutritive, such as ice, clay, chalk, dirt, or sand) Rumination Disorder (characterized by effortless regurgitation of most meals following consumption) Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder Anorexia Nervosa (restricting type or binge-eating/purging type) Bulimia Nervosa Binge-Eating Disorder Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder Unspecified Feeding or Eating Disorder Elimination Disorders • Enuresis: repeated inability to control urination (nocturnal, diurnal, or combined) • Encopresis: voluntary or involuntary fecal soiling in children who have usually already been toilet trained (w or w/o constipation and overflow incontinence) • Other Specified Elimination Disorder (w/urinary or w/fecal symptoms) • Unspecified Elimination Disorder (w/urinary or w/fecal symptoms) Sleep-Wake Disorders • • • • • Insomnia Disorder Hypersomnolence Disorder Narcolepsy (a chronic neurological disorder caused by the brain's inability to regulate sleep-wake cycles normally. People with narcolepsy often experience disturbed nocturnal sleep and an abnormal daytime sleep pattern, which often is confused with insomnia. Narcoleptics, when falling asleep, generally experience the REM stage of sleep within 5 minutes, while most people do not experience REM sleep until an hour or so later.) Breathing Related Sleep Disorders (apnea, etc.) Parasomnias (sleep walking type, sleep terror type, restless legs syndrome, etc.) Sexual Dysfunctions • • • • • • • • • Delayed Ejaculation Erectile Disorder Female Orgasmic disorder Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder Male Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder Premature Ejaculation Substance/Medication Induced Sexual Dysfunction Other Specified Sexual Dysfunction Unspecified Sexual dysfunction Gender Dysphoria • • • Gender Dysphoria (a formal diagnosis used to describe people who experience significant dysphoria (discontent) with the sex they were assigned at birth and/or the gender roles associated with that sex. Affected individuals are commonly referred to as transsexual or transgender. Evidence suggests that people who identify with a gender different from the one they were assigned at birth may do so not just due to psychological or behavioral causes, but also biological ones related to their genetics, the makeup of their brains, or prenatal exposure to hormones) Other Specified Gender Dysphoria Unspecified Gender Dysphoria Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders • • • • • • • • Oppositional Defiant Disorder Intermittent Explosive Disorder Conduct Disorder (childhood or adolescent onset) Antisocial Personality Disorder (characterized by a pervasive pattern of disregard for, or violation of, the rights of others that begins in childhood or early adolescence and continues into adulthood: dual coded here and in Personality Disorders section) Pyromania Kleptomania Other specified Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders Unspecified Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders • Categorized by drug: use disorder, intoxication, withdrawal and other specified and unspecified • Includes the following: alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, hallucinogen (including hallucinogen persisting perception disorder), inhalant, opioid, sedative, hypnotic and anxiolytic, stimulant, tobacco, and other or unknown substance • Non-Substance-Related Disorder (Gambling Disorder) Neurocognitive Disorders • • Delirium (an acute mental disturbance characterized by confused thinking and disrupted attention usually accompanied by disordered speech and hallucinations) Due to: substance intoxication, substance withdrawal, medication induced, due to medical condition, other) Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders (previously characterized as “dementia”): a usually progressive condition marked by deteriorated cognitive functioning often with emotional apathy) Due to: Alzheimers, Frontotemporal lobar degeneration, Lewy bodies, vascular disturbance, traumatic brain injury, HIV infection, Prion disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, other medical conditions, multiple etiologies, or unspecified) Personality Disorders • • • • • A class of social disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating markedly from those accepted by the individual's culture. These patterns develop early, are inflexible and are associated with significant distress or disability. Cluster A: Paranoid, Schizoid (characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, and apathy), Schizotypal (characterized by a need for social isolation, anxiety in social situations, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs) Cluster B: Antisocial, Borderline (a disordered behavior pattern with onset by early adulthood that is characterized by multiple types of psychological instability and impulsiveness, often involves fear of abandonment and a risk of suicide, and may ameliorate with age), Histrionic, Narcissistic Cluster C: Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive-Compulsive Other (due to medical condition, other specified and unspecified) Paraphilic (the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, or individuals) Disorders • • • • • • • • • Voyeuristic Disorder Exhibitionistic Disorder Frotteuristic Disorder (characterized by an interest in rubbing, usually one's pelvis or erect penis, against a non-consenting person for sexual gratification. It may involve touching any part of the body including the genital area) Sexual Masochism Disorder Sexual Sadism Disorder Pedophilic Disorder (exclusive, nonexclusive, attracted to males, females, both and/or limited to incest) Fetishistic Disorder Transvestic Disorder Other specified and Unspecified Other Mental Disorders • Specified due to a medical condition • Unspecified due to a medical condition • Other or Unspecified Medication Induced Movement Disorders and Other Adverse Effects of Medication • Neuroleptic-Induced Parkinsonism (characterized by tremor, hypokinesia, rigidity, and postural instability) • Other Medication-Induced Parkinsonism • Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: a life-threatening neurological disorder most often caused by an adverse reaction to neuroleptic or antipsychotic drugs. NMS typically consists of muscle rigidity, fever, autonomic instability, and cognitive changes such as delirium. • Medication-Induced Acute Dystonia (sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures) • Medication-Induced Acute Akathisia (characterized by unpleasant sensations of inner restlessness that manifests itself with an inability to sit still or remain motionless) Medication Induced Movement Disorders and Other Adverse Effects of Medication (Cont.) • Tardive Dyskinesia: a disorder resulting in involuntary, repetitive body movements. In this form of dyskinesia, the involuntary movements are tardive, meaning they have a slow or belated onset. This neurological disorder frequently appears after long-term or high-dose use of antipsychotic drugs, or in children and infants as a side effect from usage of drugs for gastrointestinal disorders. • Tardive Dystonia • Tardive Akathisia • Medication-Induced Postural Tremor • Other Medication-Induced Movement Disorder • Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome • Other Adverse Effect of Medication Other Conditions That May Be a Focus of Clinical Attention • Relational Problems • Abuse and Neglect (incl. child physical abuse, child sexual abuse, child psychological abuse and child neglect as well as adult maltreatment, spousal (partner) abuse and non-spousal (partner) abuse) • Educational and Occupational Problems • Housing and Economic Problems • Other Problems Related to Social Environment • Problems Related to Crime or the Legal System • Other Health Service Encounters for Counseling and Medical Advice • Problems Related to Other Psychosocial, Personal and Environmental Circumstances • Other Circumstances of Personal History Current Perspectives • Medical Perspective: psychological disorders are sicknesses and can be diagnosed, treated and cured. • Bio-Psycho-Social Perspective: assumes biological, psychological and sociocultural factors combine to interact causing psychological disorders. The Biopsychosocial Approach to Psychological Disorders The Biopsychosocial Approach to Psychological Disorders The Biopsychosocial Approach to Psychological Disorders The Biopsychosocial Approach to Psychological Disorders SANE OR INSANE ? • A LEGAL TERM USED TO DETERMINE ONES ABILITY TO STAND TRIAL ; ALSO INFERS ONES MENTAL STATE DURING THE TIME THEY COMITTEDTHE CRIME; IS NOT USED IN THE FIELD OF PSYCHOLOGY, ONLY IN LAW Anxiety Disorders http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/anxiety-disorders.html • a group of conditions where the primary symptoms are anxiety or defenses against anxiety. • the patient fears something awful will happen to them. • They are in a state of intense apprehension, uneasiness, uncertainty, or fear. • Brain area??(a-------) Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) • An anxiety disorder in which a person is continuously tense, apprehensive and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal. • The patient is constantly tense and worried, feels inadequate, is oversensitive, can’t concentrate and suffers from insomnia. Phobias • A person experiences sudden episodes of intense dread. • Must be an irrational fear. • Phobia List • agoraphobia Panic Disorder • An anxiety disorder marked by a minuteslong episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking and other frightening sensations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Sheldon has OCD • Persistent unwanted thoughts (obsessions) cause someone to feel the need (compulsion) to engage in a particular action. • compulsion • Obsession about dirt and germs may lead to compulsive hand washing. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Post-traumatic Stress Disorder a.k.a. PTSD • Flashbacks or nightmares following a person’s involvement in or observation of an extremely stressful event. • Memories of the event cause anxiety. Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/somatoform-disorders.html • Occur when a person manifests a psychological problem through a physiological symptom. • Two types…… Illness Anxiety Disorder (Used to be termed Hypochondriasis) • Has frequent physical complaints for which medical doctors are unable to locate the cause. • They usually believe that the minor issues (headache, upset stomach) are indicative are more severe illnesses. Conversion Disorder • Report the existence of severe physical problems with no biological reason. • Like blindness or paralysis. Pol Pot Dissociative Disorders • These disorders involve a disruption in the conscious process. Dissociative Identity Disorder example #2 • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. Depressive Disorders http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/mood-disorders.html • Common symptoms include a depressed mood, which includes feeling sad, and having less interest or pleasure in things that are normally enjoyable. Other core symptoms include low self-esteem, guilt, tiredness, anxiety or pessimism, and sometimes thinking about suicide. Some changes are more physical, such as changes in how much and when a person eats and sleeps, misusing drugs or alcohol, or complaining of mental or physical fatigue. Major Depressive Disorder • Unhappy for at least two weeks which may have no apparent cause. • Depression is the common cold of psychological disorders. • May be seasonal (formerly S.A.D.) Persistent Depressive Disorder (Formerly Dysthymic Disorder) • Suffering from mild depression every day for at least two years. Depression Depression Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder • Severe form of premenstrual syndrome experienced by about 2% of women. • Like PMS, premenstrual dysphoric disorder follows a predictable, cyclic pattern. • Symptoms include sadness, anxiety, anger, despair, and/or irritability. Bipolar Disorder Todd 1 Todd 2 Todd 3 • Formerly manic depression. • Involves periods of depression and manic episodes. • Manic episodes involve feelings of high energy (but they tend to differ a lot…some get confident and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. Bipolar Disorder • Bipolar Disorder –Mania (manic) • Overtalkative, overactive, elated, little need for sleep, etc. –Bipolar disorder and creativity Bipolar Brain Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders The Biological Perspective • Genetic Influences – Mood disorders run in families • Heritability • Linkage analysis • Biochemical influences – Norepinephrine and serotonin Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders The Biological Perspective Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders The Biological Perspective Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders The Biological Perspective Understanding Depressive Disorders The Social-Cognitive Perspective • Negative Thoughts and Moods Interact – Self-defeating beliefs • Learned helplessness • Overthinking – Explanatory style • Stable, global, internal explanations Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Depressive Disorders Explanatory Style Personality Disorders http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/personality-disorders.html • Well-established, maladaptive ways of behaving that negatively affect people’s ability to function. • Dominates their personality. Antisocial Personality Disorder despite the use of the outdated terminology-- • Lack of empathy. • Little regard for other’s feelings. • View the world as hostile and look out for themselves. • Lack impulse control,(frontal lobe) take action without thinking about consequences • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o aTfdKYbudk Histrionic Personality Disorder • Needs to be the center of attention. • Whether acting silly or dressing provocatively. Narcissistic Personality Disorder http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PuB_ng5uVaI&list=PL935C8510E8B3A9FA • Having an unwarranted sense of self-importance. • Thinking that you are the center of the universe. North Dakota Null-Hypothesis Brain Inventory 1. I salivate at the sight of mittens. 2. If I go into the street, I’m apt to be bitten by a horse. 3. Some people never look at me. 4. Spinach makes me feel alone. 5. My sex life is A-okay. 6. When I look down from a high spot, I want to spit. 7. I like to kill mosquitoes. 8. Cousins are not to be trusted. 9. It makes me embarrassed to fall down. 10. I get nauseous from too much roller skating. 11. I think most people would cry to gain a point. 12. I cannot read or write. 13. I am bored by thoughts of death. 14. I become homicidal when people try to reason with me. 15. I would enjoy the work of a chicken flicker. 16. I am never startled by a fish. 17. My mother’s uncle was a good man. 18. I don’t like it when somebody is rotten. 19. People who break the law are wise guys. 20. I have never gone to pieces over the weekend. 21. I think beavers work too hard. 22. I use shoe polish to excess. 23. God is love. 24. I like mannish children. 25. I have always been disturbed by the sight of Lincoln’s ears. 26. I always let people get ahead of me at swimming pools. 27. Most of the time I go to sleep without saying goodbye. 28. I am not afraid of picking up door knobs. 29. I believe I smell as good as most people. 30. Frantic screams make me nervous. 31. It’s hard for me to say the right thing when I find myself in a room full of mice. 32. I would never tell my nickname in a crisis. 33. A wide necktie is a sign of disease. 34. As a child I was deprived of licorice. 35. I would never shake hands with a gardener. 36. My eyes are always cold. Etiology of Schizophrenia ( the study of causation) #27: http://www.learner.org/resources/series142.html?pop=yes&pid=1575# http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/schizophrenia.html genetics, abnormal brain structure, and biochemistry(excess of dopamine) Diathesis-stress hypothesis – Genetic factors place the individual at risk, but environmental stress factors transform this potential into an actual schizophrenic disorder Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 Schizophrenic Disorders 26: http://www.learner.org/resources/series142.html?pop=yes&pid=1575# • About 1 in every 100 people are diagnosed with schizophrenia. Symptoms of Schizophrenia 1. Disorganized thinking. 2. Disturbed Perceptions 3. Inappropriate Emotions and Actions Disorganized Thinking • The thinking of a person with Schizophrenia is fragmented and bizarre and distorted with false beliefs. • Disorganized thinking comes from a breakdown in selective attention.- they cannot filter out information. Delusions (false beliefs) • Delusions of Persecution • Delusions of Grandeur Disturbed Perceptions Beautiful Mind clip • hallucinationssensory experiences without sensory stimulation. Inappropriate Emotions and Actions • Laugh at inappropriate times. • Flat Affect • Senseless, compulsive acts. • Catatoniamotionless Waxy Flexibility Positive v. Negative Symptoms Positive Symptoms •Presence of inappropriate symptoms Negative Symptoms •Absence of appropriate ones. Differing Faces of Schizophrenia (no longer subtypes) Realistic Schizophrenic Experience Disorganized Schizophrenia • disorganized speech or behavior, or flat or inappropriate emotion. • Clang associations • "Imagine the worst Systematic, sympathetic Quite pathetic, apologetic, paramedic Your heart is prosthetic" Paranoid Schizophrenia • preoccupation with delusions or hallucinations. • Somebody is out to get me!!!! Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat affect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements Undifferentiated Schizophrenia Putting it all together-could Harry Potter been schizophrenic??? • Many and varied Symptoms. Other Disorders • Paraphilias (pedophilia, zoophilia, hybristophilia) • Fetishism • sadist, masochist • Eating Disorders • Substance use disorders • ADHD The Rosenhan Study Rosenhahn Study • Rosenhan’s associates were Malingering symptoms of hearing voices. • They were ALL admitted for schizophrenia. • None were exposed as imposters. • They all left diagnosed with schizophrenia in remission. • What are some of the questions raised by this study? Do “Mental Disorders” really exist? • Thomas Szasz: mental illness is a myth • labeling: gives society the right to treat what are really social problems • Once labelled, people can be treated for being “different” Perspectives and Disorders Psychological School/Perspective Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic Cause of the Disorder Internal, unconscious drives Humanistic Failure to strive to one’s potential or being out of touch with one’s feelings. Behavioral Reinforcement history, the environment. Cognitive Irrational, dysfunctional thoughts or ways of thinking. Sociocultural Biomedical/Neuroscience Dysfunctional Society Organic problems, biochemical imbalances, genetic predispositions.