* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EVOLUTION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
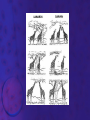
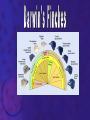
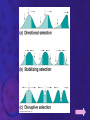
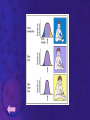
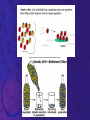
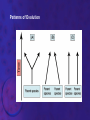
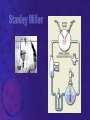
EVOLUTION Prof. Benilda Ramos-Butron What is evolution? • Refers to changes in the populations, species or groups of species • Variation of the frequency of heritable traits that appear from one generation to the next • Changes in allele frequencies over time Two areas of evolutionary study 1. Microevolution • Describes the details of how populations of organisms change from generation to generation and how new species originate 2. Macroevolution • Describes patterns of changes in groups of related species over broad periods of geologic time • Determines phylogeny Evidence of Evolution 1. Paleontology – provides fossils that reveal the prehistoric existence of extinct species 2. Biogeography – uses geography to describe the distribution of species 3. Embryology – reveals similar stages in ontogeny among related species 4. Comparative anatomy – describes two kinds of structures that contribute to the identification of evolutionary relationship among species • Homologous structures • Analogous structures Evidences of Evolution 5. Molecular Biology/Biochemistry – examines the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of DNA and proteins from different species Earliest Advocates of Evolutionary Ideas 1. Jean Lamarck • Use and disuse • Inheritance of acquired characteristics • Natural transformation of species 2. Charles Darwin • Theory of Natural Selection or known as the “survival of the fittest” 3. Neo-Darwinism or Synthetic Theory of Evolution or Modern Synthesis Explain the difference of the theories of Lamarck and Darwin given the illustration that follows. Natural Selection • Is the difference in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population as a result of their interaction with the environment • Arguments of Darwin for Natural Selection Population possess an enormous reproductive potential Population size remains stable Resources are limited Individuals compete for survival There is variation among individuals in a population Much variation is heritable Only the most fit individuals survive Evolution occurs as advantageous traits accumulate Kinds of Selection According to Darwin 1. Stabilizing selection 2. Directional selection 3. Disruptive selection or Diversifying selection Sources of Variation 1. Mutations – provide the raw material for new variation 2. Sexual reproduction – creates individuals with new combinations of alleles • Crossing over, independent assortment and random joining of gametes 3. Diploidy 4. Outbreeding – mating with unrelated partners 5. Balanced polymorphism – is the maintenance of different phenotypes in a population • Heterozygote advantage, hybrid vigor, frequency adapted selection Causes of Changes in Allele Frequencies 1. Natural Selection – is the increase or decrease in allele frequencies due to the impact of the environment 2. Mutations – introduce new alleles that may provide a selective advantage 3. Gene flow – describes the introduction or removal of alleles from the population when individuals emigrate or immigrate 4. Genetic drift – random increase or decrease of alleles • Founder effect • Bottleneck Causes of Changes in Allele Frequencies 5. Nonrandom mating – occurs when individuals choose mates based upon their particular traits • Inbreeding • Sexual selection Interpret the diagram that follows regarding speciation. Speciation • Formation of new species • Processes: Allopatric speciation – begins when a population is divided by a geographic barrier Sympatric speciation – is the formation of new species without the presence of a geographic barrier (balanced polymorphism, polyploidy, hybridization) Adaptive radiation – is the relative rapid evolution of many species from a single ancestor Patterns of Evolution Patterns of Evolution 1. Divergent Evolution – describes two or more species that originate from a common ancestor 2. Convergent Evolution – describes two unrelated species that share similar traits 3. Parallel Evolution – describes two unrelated species or two related lineages that have made similar evolutionary changes after their divergence from a common ancestor Patterns of Evolution 4. Coevolution – is the tit-for-tat evolution of one species in response to new adaptations that appear in another species The Origin of Life • • Chemical evolution – is the study how life began Heterotroph theory – proposes that he first cells were heterotrophs SUCCESSION: 1. The earth and its atmosphere formed • Primordial atmosphere consisted of CO, CO2, H2, N2, H2O, S, HCl and HCN but little or no oxygen The Origin of Life 2. The primordial seas formed. 3. Complex molecules were synthesized • Formation of organic soup (acetic acid, formaldehyde, amino acids) • Energy provided from UV, lightning, radioactivity, and heat • A.I. Oparin and J.B.S. Haldane proponents of an oxygen-less primitive atmosphere • Stanley Miller performed experiment to prove Oparin and Haldane’s theory The Origin of Life 4. Polymers and self-replicating molecules were synthesized • Proteinoids – abiotically produced polypeptides 5. Organic molecules were concentrated and isolated into protobionts • Protobionts – precursors of cells • Microspheres and coacervates 6. Primitive heterotrophic prokaryotes formed 7. Primitive autotrophic prokaryotes were formed The Origin of Life 8. Oxygen and the ozone layer formed and abiotic chemical evolution ended 9. Eukaryotes formed (Endosymbiotic theory) In the present day, do you think evolution happens? If yes, what factors do you think pushes evolution of organisms? The End