* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Teaching Notes
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
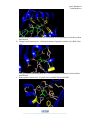
Level: Advanced Teaching Notes Exploring a Protein Structure in the RCSB PDB: Major Histocompatibility Complex Learning Goals: 1. Visualize the structure of a given molecule using RCSB PDB resources. 2. Explore the structure to understand its structure function relationships Educational Standards A. Common Core a. Craft and Structure i. RI.9-10.4 ii. RI.11-12.4 b. Integration of Knowledge and Ideas i. RI.9-10.7 ii. RI.11-12.7 B. Next Generation Science Standards a. Practices i. 8. Obtaining, Evaluating and Communicating Information b. Crosscutting Concepts i. 3. Scale, proportion and quantity ii. 4. Systems and system models iii. 6. Structure and function c. Disciplinary Core Ideas i. LS1.A: Structure and Function ii. PS2.B: Types of Interactions C. Advanced Placement Biology - Essential Knowledge (EK), Learning Objectives (LO), Science Practices (SP) a. EK 4.A.1 i. LO 4.2, SP 1.3 ii. LO 4.3, SP 6.1, 6.4 Teaching Notes: About Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC): 1. Structure: a. The MHC (Class I) is composed of two protein chains – Class I Histocompatibility Antigen (HLA) and beta-2 microglobulin. b. The HLA chain has two domains – one that binds the peptide antigen in a cleft with a beta sheet at its base and in between two helices. c. The other domain is a beta sandwich (Immunoglobulin domain) that interacts with another immunoglobulin domain structure – the beta-2 microglobulin. 2. Function: a. The antigenic peptide binds to the cleft in the HLA chain. (Note: in the Class II MHC molecule the antigen binding cleft is composed of two different chains). Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2015 Level: Advanced Teaching Notes MHC I, PDB ID 1hsa An gen b2 microglobulin An gen MHC II, PDB ID 1dlh a chain a chain b chain The appropriate T-Cell Receptor binds to both the MHC molecule and bound antigen in a specific way to trigger signals in the T-cell. Answers to Questions in Exercise: Q1. In PDB entry 1hla, how many polymer chains are there? What are they? A1: There are 3 protein chains - HLA, beta-2 microglobulin and the antigen peptide Q2. Where are the Cys residues located? Comment about how they are contributing to the stability of the structure. A2: A single S-S bond stabilizes each of the immunoglobulin domains. In addition, there is an S-S bond between one of the helices surrounding the antigen binding cleft and the beta sheet forming the base of the cleft. This bond stabilizes the antigen-binding cleft. Q3. Based on your explorations of the binding neighborhood of the peptide from HIV-1 GP120 protein in PDB entry 1hhg, list 3 types of interactions that are stabilizing the peptide in the MHC I molecule. List the residues involved in these interactions and show these interactions in 2-3 figures. A3: There are several different interactions between the peptide and the MHC I molecule. Examples of these interactions are listed below: a. Hydrogen bonds – between amino terminus of peptide (residue 1) to Tyr171, Tyr 159, Glu63 and Tyr7 of MHC-I; Tyr 59 is hydrogen bonded to Tyr 171 of MHC-I Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2015 Level: Advanced Teaching Notes All interacting residues around the N-terminus of the peptide are colored in yellow and labeled. b. Charge based interactions – Carboxy terminus of peptide (residue 9) to MHC-I Lys 146 The Lys residue interacting with the C-terminal peptide residue is colored yellow and labeled. c. Hydrophobic interactions –Peptide Leu2 and MHC Phe9 and Val67 Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2015 Level: Advanced Teaching Notes Residues participating in the hydrophobic interactions around Leu2 of the peptide are shown in yellow and labeled. Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2015