* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - TGGS Science
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
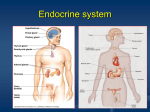
Biology 1 Basic Revision Classification What are the five kingdoms of life and the differences between them? Do scientists consider viruses to be living things? What does “chordata” mean? What three characteristics are used to divide vertebrates into classes? Why is a duck-billed platypus hard to classify? What does “binomial classification” mean? Variation What does variation between individuals in a species mean? What two factors cause variation (give examples)? What is continuous and discontinuous variation (give examples)? What is a normal distribution (sketch a graph)? What is chemosynthesis? How are animals adapted to cold regions like the Arctic? How are animals adapted to hot regions like the Sahara desert? Natural Selection What does natural selection (or survival of the fittest) mean? What does evolution mean? What evidence is there for evolution? How do scientists validate new evidence? Speciation and Genes What does speciation mean? Use the example of gulls on islands to explain. Label this diagram. How many chromosomes are found normally in a human? Describe the shape of the DNA. Describe the bond between the strands of DNA. Genetic Diagrams What does genotype and phenotype mean? What does homozygous and heterozygous mean? Two people have a child. B = Blue eyes. B = brown eyes, Draw a Punnett square to show the results of a father with heterozygous genes and a mother with homozygous recessive genes. Explain what the results tell you.* Genetic Disorders What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? What are the symptoms of sickle cell anaemia? Are these diseases caused by a dominant or recessive gene? (Note that genetic diseases can be either). Homeostasis What is homeostasis? What is thermoregulation? What is osmoregulation? What is negative feedback? Explain how the body controls temperature (4 ways).* What part of the brain controls temperature responses? What are hormones? What parts of the body release hormones? The Nervous System Label this neurone (nerve cell). What direction does the nerve signal travel in? What does the myelin sheath do? What are the three types of nerve cell? Explain how the nervous system allows us to carry out a controlled response by completing this diagram: Brain Motor Sensor How is a reflex action different to this?* Insulin and Diabetes What are the symptoms of diabetes? What does insulin do? What causes type 1 diabetes? What can cause type 2 diabetes? How is diabetes treated or managed (refer to the specific types of diabetes)?* Plant Growth Hormones What is positive tropism? What is geotropism and phototropism? What do auxins do? What do gibberellins do? How do hormones cause plants to bend towards light? How do hormones cause plants to bend towards Earth? (The answer is not gravity). How are hormones used in the agricultural industry to improve production?* Drugs What is a drug? What is a narcotic? What is the difference between a stimulant and a depressant? What are hallucinogens? What are the dangers of smoking? (Think about tar, hot smoke and nicotine). What are the dangers of alcohol? Organ Transplants What are the ethical consideration surrounding organ transplants? Antiseptics and Antibiotics How are infectious diseases spread? (Seven ways) How does the body prevent infection? What are antiseptics antibiotics? (They aren’t the same thing). What is MRSA and how does it develop? Energy and Biomass What is biomass? How is energy lost from a foodchain? Parasitism and Mutualism What is a parasite (give examples)? What is a mutualist (give examples)? Human Activity and the Environment Why is an increasing human population a problem? What materials can we recycle? What problems are there with recycling? Indicator Species What is an indicator species? What species can indicate good quality air and water? What species can indicate poor quality air and water? The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles What is eutrophication? What four type of bacteria are involved in the nitrogen cycle? How else is nitrogen released or absorbed from the atmosphere? Draw the carbon cycle diagram.