* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operational Strategies: Innovation
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Diffusion of innovations wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
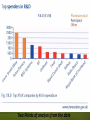
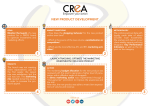
Operational Strategies: Innovation A2 Business Studies Aims and Objectives Aim: • Understand innovation as an operational strategy. Objectives: • Define innovation and R&D • Describe the R&D process • Analyse functional areas relationship to innovation • Evaluate functional areas relationship to innovation Starter • Think of 4 products which have recently been launched onto the market. • How have these influenced the lives of consumers? • How have competitors reacted to these new products? • What process have all of these products been through? Research and Development • Define research and development. Definition: The scientific research and technological development used to create a new product or process. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzkaEUEFsoQ Research and Development Process Idea Generation Organisations that have enterprising culture, may involve all employees in process. E.g. Google Idea Screening Considering the practical nature of the idea in terms of resources available and customers needs. Concept Testing Business forms focus groups to gauge customer reactions to the product/service and its functions. Development of Ideas Responses from consumers used to develop viable ideas. Business Analysis The business judges whether each has idea has the potential to make a profit. Business should consider product portfolio, will it attract new customers or just existing ones to switch products (cannibalisation). Product Development Developing products into working prototypes which can be tested. Test Marketing Launching a new product to a small target market to identify any final adjustments. Business must be careful as competitors will see for first time. Two Points of analysis from the data Research and Development • Why should businesses invest in R&D? • What are the likely costs to a business of R&D? Research and Development Analysis - Product kept at cutting edge - Creates a competitive advantage - Allows for premium pricing - Helps maintain market position or increase market share - Opportunity costs e.g. money could be used to retrain staff, launch marketing campaign etc. - Large sums of money invested without guaranteed success Research and Development Evaluation • However effective or creative R&D is it will not satisfy the operational objectives. • Only when the R&D leads to a successful economic outcome that it leads to a comp. adv. • Successful outcomes only come from extensive R&D and even then, product success is not guaranteed! Innovation • R&D is part of the process of innovation. • Can Microsoft still innovate using R&D to build a comp. advantage with the rise of Apple and Sony? • Microsoft spends $9bn (£5.5bn) a year on research and development - and yet its rivals are often seen as more innovative. Is this the case? • http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-12582357 • http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-12581442 Innovation • Define Innovation Definition: The launch of a new product or process onto a market. • Task: Brainstorm what you feel the risks and rewards are of committing to R&D and Innovating new products. Risks Rewards If new product fails could affect brand image Build reputation as innovative business Heavy time and resources commitment, no guarantee of success. Development of USP, and competitive adv. Potential loss of focus on business. Charge premium prices Competitors reaction Efficiency improvements in production Impacts of Innovation & R&D • Round Robin • Consider the impacts of a business embarking on a costly R&D innovation strategy to launch a new product on functional areas of the business. – Marketing – Finance – Human Resources Marketing Finance • Feedback HR Impacts of Innovation & R&D on Marketing Marketing may help identify target market May gather consumer opinions May assist in using a market led approach Will design marketing mix for product Communicate new product to customer, so it is vital communication is good with operations. Impacts of Innovation & R&D on Finance Finance must set budgets for R&D and communicate these whilst monitoring them. Costing of new products/processes Work with marketing to set pricing structures Profit, sales, cots of new products Impacts of Innovation & R&D on Human Resources R&D is likely to have workforce planning issues as there could be a need for new skilled workers to manufacture a new product. Reduce workforce size, due to manufacturing innovations. Impacts of Innovation & R&D on Functional Areas Vital for all functions to have an input from the outset. This simultaneous development and engineering can potentially save time, money and result in a more efficient process. Marketing Finance HR