* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex Cells and Inheritance
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
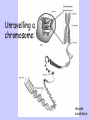
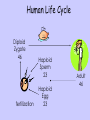
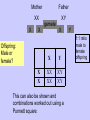
Sex Cells and Inheritance Cells- more on the nucleus Animal and plant cells contain a nucleus. The nucleus controls cell activities including cell division. It also contains the genetic information needed to produce a new cell. The information is organized into units called genes. Our genes are on chromosomes Unravelling a chromosome: Access excellence Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes come in pairs. Human body cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. This gives a diploid number of 46. Human gametes (sperm and egg cells) contain 23 chromosomes. This is the haploid number. Reproduction Revision Complete the following sentences Pupil Activity Another name for sperm and egg cells is gametes ________ These sex cells join to make one cell during fertilization __________ This cell grows into a baby by multiplying & dividing __________________ many times. Each body cell in the baby contains 23 ____ pairs of chromosomes. One of the chromosomes in each pair comes from the mother _______, the other father from the _______ Human Life Cycle Diploid Zygote 46 fertilization Haploid Sperm 23 Haploid Egg 23 Adult 46 Genes A characteristic is controlled by the two forms of a gene present in an individual. (but the particular combinations are limited by the genetic makeup of your parents). The different forms of a gene are called alleles. Genetics Buzzwords physical appearance of an organism. the set of genes (alleles) that an organism possesses different forms of the same gene when two alleles (gene types) are identical when the two alleles are different allele which controls the characteristic whenever it is present. BB or Bb allele whose characteristics only show up when it is present on both chromosomes bb Boy or Girl? The sex of a child is determined by specific chromosomes called X and Y chromosomes. In humans, each male gamete may have an X or a Y chromosome, while each female gamete has an X chromosome. Female Male Body cells are XX All X Body cells are XY gametes X or Y Mother Father XX XY X X Offspring: Male or female? X X gamete X X Y XX XX XY XY This can also be shown and combinations worked out using a Punnett square: Y 1:1 ratio male to female offspring Genes and Genotypes • Genotype: set of genes that an organism possesses • Each organism has two forms of the same gene -one inherited from mother -one inherited from father • We can say that ‘Organisms possess two alleles for each different gene’ Genotypes and Symbols Each allele is represented by a letter -capital letter if the allele is dominant (A) -lower case letter if the allele is recessive (a) Each organism will have two letters -1 represents the allele it receives from its mother -1 represents the allele it receives from its father Height in Pea Plants T = tall (dominant) t = short (recessive) A pea plant can be: TT = homozygous tall Tt = heterozygous tall (because T is dominant to t) tt = homozygous short Gene combinations The simplest genetic cross involves one characteristic and is called a monohybrid cross. In this the parents (P) are crossed (bred) with each other, and the offspring (F1 generation) observed and counted. Parents Phenotypes Genotypes Gametes Tall (Bred with) TT X all T F1 genotype F1 phenotype Dwarf tt all t Tt all tall