* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes: Chromosomes and Meiosis Gametes have half the number of
Survey
Document related concepts
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
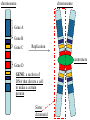
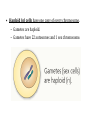
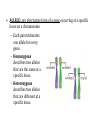
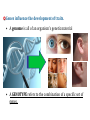
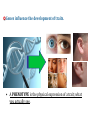
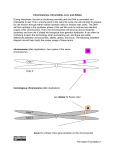
Notes: Chromosomes and Meiosis Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. chromosome chromosome Gene A Gene B Gene C Replication centromere Gene D GENE: a section of DNA that directs a cell to make a certain protein Sister chromatid You have somatic cells and gametes. Somatic (body) cells: • Make up body tissues & organs • DNA in these cells are NOT passed on to offspring body cells You have somatic cells and gametes. Gametes: • Are sex cells like sperm and egg • DNA in these cells ARE passed on to offspring sex cells (sperm) sex cells (egg) Each cell has autosomes and sex chromosomes. • Your body cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 1. (22) AUTOSOMES contain genes that determine body information (hair color, eye color, hair texture, etc.) 2. (1) pair of SEX CHROMOSOMES determine sex (XX=female; XY=male). 3. HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS of chromosomes have the same structure (size, genes) Body cells are diploid; gametes are haploid. • Fertilization between egg and sperm occurs in sexual reproduction. • Diploid (2n) cells have two copies of every chromosome. – Each comes from each parent • Haploid (n) cells have one copy of every chromosome. – Gametes are haploid. – Gametes have 22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome. Mitosis • Produces genetically identical cells • Results in diploid cells • Occurs throughout organism’s lifetime • Asexual reproduction Meiosis • Produces genetically unique cells • Results in haploid cells • Occurs during certain times of one’s life cycle • Sexual reproduction • ALLELE: any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. Genes influence the development of traits. • A genome is all of an organism’s genetic material • A GENOTYPE refers to the combination of a specific set of genes. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus/location. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus/location. Genes influence the development of traits. • A PHENOTYPE is the physical expression of a trait; what you actually see. • Alleles can be represented using letters. – Dominant alleles are expressed as the phenotype; the stronger allele; represented by capital letters – Recessive alleles are considered the “weaker allele” and is expressed only when two copies are present; lowercase letters