* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell permeable Foxp3 protein converts CD4 T cells to suppressor
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
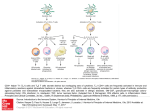
Title Regulation of T cells with Foxp3 suppresses allergic and autoimmune disease Abstract Regulatory T cells (Treg) are a very powerful component of the immune system, as they have the capacity to down-modulate T cell-mediated immune responses. Foxp3 is a key transcription factor in Tregs related with differentiation, function, and survival of CD4+CD25+ Tregs. Foxp3-transduced T cells have been studied for conversion of CD4+CD25- T cells to CD4+CD25+ Treg cells as well as for inhibition of T cell activation and proliferation. To study about Foxp3 function in T cells, we have generated a recombinant protein of Foxp3 combined with previously identified novel PTD (protein transduction domain) of Hph-1. Hph-1-Foxp3 can convert CD4+CD25- T cells to suppressor cells as well as inhibit T cell activation and proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Sever systemic autoimmune response in Foxp3-mutant scurfy mice were significantly reconstituted by i.p. injection and also treatment of Hph-1-Foxp3 suppressed scurfy CD4 T cell mediated-inflammatory bowl disease (IBD). Furthermore, Foxp3-mediated T cell anergy and increase of suppressor cells strongly inhibited OVA-induced lung inflammation by intra-nasal delivery of Foxp3. These results emphasize the possibility of Foxp3 as a therapeutic agent in allergic and autoimmune diseases.