* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Clinical Microbiology
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
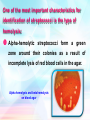
Clinical Microbiology (MLCM- 201) Prof. Dr. Ebtisam.F. El Ghazzawi. Medical Research Institute (MRI) Alexandria University OUTCOMES By the end of this lecture the Student should be able to understand Streptococci Types ,Shape Characteristics, pathology and Diagnosis. The streptococci catalase negative are gram-positive spherical bacteria that characteristically form pairs or chains during growth. They are widely distributed in nature. Some are members of the normal human flora, others are associated with important human diseases. Streptococcus pyogenes Gram stain Streptococcus pneumoniae Gram stain One of the most important characteristics for identification of streptococci is the type of hemolysis: Alpha-hemolytic streptococci form a green zone around their colonies as a result of incomplete lysis of red blood cells in the agar. Alpha hemolysis and beta hemolysis on blood agar Beta-hemolytic streptococci form a clear zone around their colonies because complete lysis of the red cells occurs. Beta-hemolysis is due to the production of enzymes (hemolysins) called Streptolysin O and Streptolysin S. Some streptococci hemolysis). are nonhemolytic (gamma Sheptococci cause a wide variety of infections. Strept. Pyogenes (group A streptococci) is a leading bacterial cause of pharyngitis and cellulitis. It is an important cause of impetigo, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis. Viridans group streptococci are the most common cause of endocarditis. a. Specimens: specimens to be obtained depend upon the nature of the streptococcal infection. A throat swab, pus or blood is obtained for culture. Serum is obtained for antibody determinates. b. Smears: smears from pus often show single cocci or pairs rather than definite chains. Smears of throat swabs are rarely contributory, because viridians streptococci are always present and have the same appearance streptococci on stained smears. as group A c. Culture: streptococci are cultured on blood agar. Incubation in 10% CO2 often speeds hemolysis. The degree and kind of hemolysis (and colonial appearance) may help place an organism in a definite group. Streptococci belonging to group A may be presumptively identified by inhibition of growth by Bacitracin. d. Antigen detection tests: Several commercial kits are available for rapid detection of group A streptococcal antigen from throat swabs. These kits use enzymatic or chemical methods to extract the antigen from the swab, then use EIA or agglutination tests to demonstrate the presence of the antigen. e. Serologic tests: A rise in the titer of antibodies to many group A streptococci antigen can be estimated. Of these antibodies the antistreptolysin O (ASO) particularly in respiratory disease can be estimated. Assignments scarlet Fever ß-Hemolytic Streptococci. Questions Complete the following :- The streptococci are gram-positive ……………negative ……………bacteria. Beta-hemolysis is due to the production of enzymes (hemolysins) called ………………. Recommended Textbooks Manual of Clinical Microbiology, Vols. 1 and 2: Eighth Edition Patrick R. Murray