* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mass Spectrometry
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Degradomics wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Sample preparation in mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
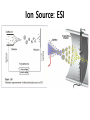
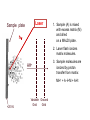
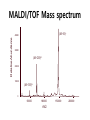
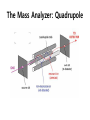
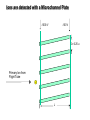
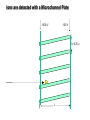
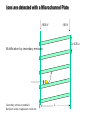
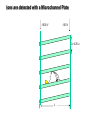
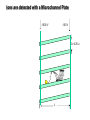
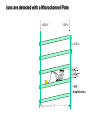
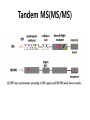
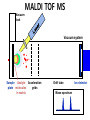
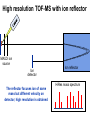
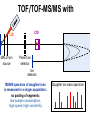
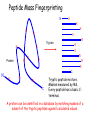
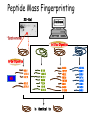
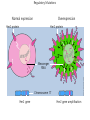
Mass Spectrometry • • • • • Widely used analytical technique Within an accuracy of 0.01% of total weight of sample and within 5 ppm for small organic molecules Unequaled sensitivity –Nanomolar range routinely (1 x 10-9M) –Femtomolar range possible (1 x 10-15M) –Attomolar range claimed (1 x 10-18M) Diversity of applications –Proteins –Oligonucleotides –Oligosaccharides –Lipids –Others Proteomics –Identification of proteins expressed under specific conditions -3 fundamental parts: Ionization source, the analyzer, the detector -Ionization source 시료분자를 이온화시키고 더 작은 이온으로 쪼갠다. -Mass analyzer 이온들을 mass-to-charge(m/z) ratio에 따라 선택적으로 분리 -Ion detector 이온 흐름을 그 양에 비례하게 전기적인 흐름으로 전환, 증폭시켜 signal을 생성 -Vacuum system Basic components to MS •Ion source –Electrospray(ESI) –Atmospheric Pressure Ionization (APCI) –Chemical Ionization (CI) –Electronic Ionization (EI) –Matrix Assisted Laser DesorptionIonization (MALDI) •Mass Selection –Quadrupole –Time of Flight (TOF) –Magnetic Sector –Ion Trap –Ion Cyclotron •Detector –Phosphor / Photo Diode –Multi-channel Plate (MCP) Ion Source: ESI Electrospray ionization(ESI) -용액 상태의 시료를 이온화(LC-MS) -기존의 방법으로는 얻기 힘들었던 intact 상태의 peptide나 단백질을 이온화 -한 개 이상의 전하를 띤 이온을 생성 Ion Source: ESI Ion Source: ESI Ion Source: MALDI Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization(MALDI) Laser m m + a a + m a m + a m a a + m m m+ m m matrix + analyte Sample support Matrix CH CH O 3 COOH C(CN)COOH CH CHCOOH OH HO HO HO -cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,5-DHB) CH O 3 Sinapinic acid (3,5-Dimethoxy-4-hydroxy cinnamic acid) Laser Sample plate hn 1. Sample (A) is mixed with excess matrix (M) and dried on a MALDI plate. 2. Laser flash ionizes matrix molecules. AH+ 3. Sample molecules are ionized by proton transfer from matrix: MH+ + A M + AH+. +20 kV Variable Ground Grid Grid Why MALDI? -Less sensitive to salts -Lower PRACTICAL detection limits -Easier to interpret spectra(less multiple charges) -Quick and easy -Higher mass detection -Higher Throughput(1000>samples per hour) MALDI/TOF Mass spectrum (M+H)+ Relative Abundance 40000 30000 (M+2H)2+ 20000 10000 (M+3H)3+ 0 50000 100000 m/z 150000 200000 The Mass Analyzer: TOF Time Of Flight(TOF) Ion Source Flight Tube 20-25 kV + + Principle: If ions are accelerated with the same potential at a fixed point and a fixed initial time and are allowed to drift, the ions will separate according to their mass to charge ratios. Calibration of the mass scale The mass-to-charge ratio of an ion is proportional to the square of its time of flight in the analyzer (“drift time”). 2 m 2t K 2 z L t L m K z = = = = = Drift time Drift length Mass Kinetic energy of ion Number of charges on ion The Mass Analyzer: TOF Ion Source Flight Tube + Detector + + The Mass Analyzer: TOF Ion Source Flight Tube + + + Detector The Mass Analyzer: Quadrupole Quadrupole(Mass filter) -4개의 molybdenum 막대로 이루어져 있으 며, 한쌍(1,2)은 DC voltage, 다른 한쌍(3,4) 은 Radio frequency voltage가 가해진다. -가해지는 전압의 진폭은 선택된 m/z에 해 당되는 ion만 ion source에서 detector까 지 통과하게 한다. - quadropole의 전압을 바꾸면서 주어진 mass범위의 이온을 scanning 한다. The Mass Analyzer: Quadrupole Detectors Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V D= 6-25 u + Primary Ion from Flight Tube L Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V + D= 6-25 u L Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V D= 6-25 u Multification by secondary emission + e- Secondary emissive materials: Beryllium oxide, magnesium oxide etc L Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V D= 6-25 u ee- e- + e- L Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V D= 6-25 u ee- e- + e- L Ions are detected with a Microchannel Plate -1000 V -100 V D= 6-25 u eee- e- e- e- e e- + e- e- ee- ~103 Amplification L Tandem MS(MS/MS) Tandem MS(MS/MS) Tandem MS(MS/MS) MALDI TOF MS Vacuum lock Vacuum system Sample Analyte Acceleration plate molecules grids in matrix Drift tube Mass spectrum Ion detector High resolution TOF-MS with ion reflector MALDI ion source Ion detector The reflector focuses ion of same mass but different velocity on detector; high resolution is obtained Ion reflector HiRes mass spectrum TOF/TOF-MS/MS with CID LID MALDI ion source Parent ion selector Ion detector MS/MS spectrum of daughter ions is measured in a single acquisition; no pasting of segments; low sample consumption, high speed, high sensitivity Ion reflector Daughter ion mass spectrum Why interested in MALDI-TOF MS 분자량 측정 큰분자량 물질 분석 혼합물 분석 : 한 종류의 성분이 아닌 몇 종류가 혼재해 있어도 분석이 가능함 미량분석 : 매우 민감하여 미량의 시료도 분석 가능 함 : 펩타이드 경우 fmol 분석 가능 데이터 분석이 쉬움 : 분자 구조가 깨어 지지 않고, 보통 다 전하를(multiple charging)띠지 않으므로 데이 터가 다른 질량 분석기에서 보다 단순하여 해석이 용이함 염의 영향이 적음 : 생체단백질 분리에 이용되는 완충용액, 염 등에 LC/MS 보다 영향을 덜 받음 분석이 신속함 : 시료와 Matrix 섞어 sample plate에 떨어뜨려 용액을 말리는 시간(약 5~10 분), MALDITOF 로 분석하는 시간 (1분 이내) 기기 사용 및 유지하기 위한 비용이 저렴 : LC/MS, GC/MS 처럼 질소 또는 아르곤 가스를 사용하지 않고, 미 량의 Matrix와 ACN, TFA등을 이용함으로 시약 비용도 저렴함 Mass Spectrometry 분석 -base peak -parent peak -radical cations -Isotopes Peptide Sequencing Biomolecule Analysis *과거에는? -Electrophoresis, chromatography, ultracentrifugation -Not very precise *MS이용하면? -Proteins, oligonucleotides, oligosaccharides, lipids -Detect modifications and sequences Peptide Mass Fingerprinting • Analytical technique for protein identification (protein sequence) • Unknown protein of interest cleaved into peptide by protease • Collection of peptides resulting from this cleavage comprise a unique identifier of the unknown protein • Mass measured with MALDI-TOF and ESI-TOF • in silico compared to the genome • Computer programs translate the known genome of the organism into proteins • Theoretically cut the proteins into peptides with the same protease (ex.Trypsin: K or R) • Calculate the absolute masses of the peptides from each protein • the masses of the peptides of the unknown protein vs the theoretical peptide masses of each protein encoded in the genome • Results statistically analyzed to find the best match In Gel Digestion & Mass Spectrometry Trypsin Digest Cut out 2D-Gel Spot Protein Peptides Peptide Mass Fingerprinting N K K R K K K R Trypsin K R Protein N K K K R K R R R C K K R C Tryptic peptide mixture. Masses measured by MS. Every peptide has a basic Cterminus. A protein can be identified in a database by matching masses of a subset of the tryptic peptides against calculated values. intact protein enzyme peptide fragments MEMEKEFEQIDKSGSWAAIYQDIRHEASDFPCRVAKLPKNKNRNRYRDVS PFDHSRIKLHQEDNDYINASLIKMEEAQRSYILTQGPLPNTCGHFWEMVW EQKSRGVVMLNRVMEKGSLKCAQYWPQKEEKEMIFEDTNLKLTLISEDIK SYYTVRQLELENLTTQETREILHFHYTTWPDFGVPESPASFLNFLFKVRE SGSLSPEHGPVVVHCSAGIGRSGTFCLADTCLLLMDKRKDPSSVDIKKVL LEMRKFRMGLIQTADQLRFSYLAVIEGAKFIMGDSSVQDQWKELSHEDLE PPPEHIPPPPRPPKRILEPHNGKCREFFPNHQWVKEETQEDKDCPIKEEK GSPLNAAPYGIESMSQDTEVRSRVVGGSLRGAQAASPAKGEPSLPEKDED HALSYWKPFLVNMCVATVLTAGAYLCYRFLFNSNT Peptide Mass Fingerprinting 2D-Gel Database “Spot removal” In Silico Digestion In Gel Digestion MS 848.1 1272.5 492.6 883.2 2978.9 812.6 1432.3 3127.1 996.8 702.4 164.9 2748.2 Is identical to 848.3 1272.7 493.2 882.6 2978.3 364.1 948.9 3128.8 3514.2 2837.1 263.9 147.4 1429.7 199.6 142.3 640.8 Post Translational Modifications(PTM’s) • PTM’s are very important in signaling as well as metabolic pathways (e.g. phosphorylation) • Often we want to know not only which modification a protein has undergone, but exactly where in the sequence the modification lies. • Many of the search engines allow for “variable” modifications, but very few at one time (combinatorialy explosive) • There is great opportunity here for robust searches that find PTM’s reliably! Protein sequence Analysis For sequencing of an entire Protein…?? Divide and Conquer !!! Deduction of Full Amino Acid Sequence of a Protein by Overlapping the Sequences Obtained from individual Peptides Edman Degradation Sequentially Removes One Residue at a Time from the Amino End of a Peptide up to 50 times Each round can be complete within 1 hr and the Edman degradation can be repeated up to 50 cycles in Practice. Lymphomas and Leukemias Regulatory Mutations Normal expression Overexpression Her2 protein Her2 protein Messenger RNA Chromosome 17 Her2 gene Her2 gene amplification