* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparative Psychology
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary psychology wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Mate choice wikipedia , lookup
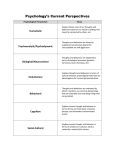
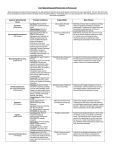
Gender differences in criminal behaviors What gender differences can you think of in terms of criminal behaviour? Evolution of crime – What is evolution, how can criminal behaviors be explained via evolutionary factors? What gender differences exist between males and females? Why do males tend to be involved in a lot more criminal activities than females? What advantages are there for risk taking behaviors? Gender differences in criminal behaviors An organism’s ability to survive depends on how well its characteristics allow it to: – Exploit the opportunities available in its environment – Avoid or deal with the threats presented by its environment We call this the organism’s fitness The fitness of an individual will be directly influenced by their reproductive success. Fitness Fitness Yummy! Gender differences in criminal behaviors Fit organisms are more likely to survive into adulthood than unfit ones. – Consequently, they are more likely to mate and have offspring – They pass on their genes to the next generation Gradually, the genes for successful characteristics spread through the population Risk taking behaviors may increase fitness in terms of predator avoidance and increased reproductive success. Gender differences in criminal behaviors Pressures of mate selection in our evolutionary past have lead to different behaviors being pre-disposed in the population. Due to intersexual selection (choosing an appropriate mate) and intrasexual selection (competing for a mate) risky behaviors are exhibited by males to increased the likelihood of attracting a sexual partner. Evolutionary differences in criminal behaviours Age crime curve- the peak of offending happens in early twenties and then falls into mid to late twenties. Why do you think that this age crime relationship exists? Daly and Wilson- 2001. Key study Identified the ‘short term horizon’. Based on the idea that male seek immediate gratification- they are not concerned with long term gains. In terms of evolution what other reason could there be for risk taking behaviours is not for sexual selection processes? Read the handout on the Daly & Wilson study and then answer the following questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What was the aim of their study? How many community areas were involved? What is a correlational analysis? What variable did D & W correlate in their investigation? What was the average life expectancy of the participants? What did D & W find in relation to life expectancy and neighbourhood specific homicides? What was the co-efficient? They found a negative correlation between life expectancy and truancy from school- how was this explained? What problems may arise when using evolutionary explanations to explain modern day behaviours? What can we conclude form Daly’s research? Write 4 evaluation points of the biological explanations-single gene?, environmental influences?, falsifying evolution explanations?, methods of investigation?, reductionist?