* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibiotic treatment of Crohn`s Disease: Does it Work?
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
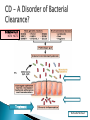
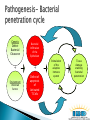
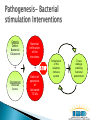
Arie Levine Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Wolfson Medical Center Oxidative Burst NCF4 NCF2 Treatment Darfeuille Michaud Defective apoptosis T cells (Bax/ BCL2 ratios ) Defective apoptosis in dendritic cells with NOD2 mutations Increased Survivin –HSP90( anti-apoptotic molecule) in mucosal T cells in Crohn’s disease Apoptosis pharmoacogenetic indices predict response to therapy Response to thiopurines correlated with apoptosis effect Ina et al. J Immunol 1999;163:1081–90 Zelinkova et al Inflamm Bowel Dis 2008 ;14:186-94 De Souza et al Gastroenterology 2012 Hlavaty et al Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007;13:372-9 Cosu etal JCC 2012 epub Genetic Defect Bacterial Clearance Bacterial Infiltration of the Epithelium + + Environment Unknown factors Defect of apoptosis of Activated T Cells Abnormal Stimulation regulation of the of the adaptive immune immune system system Tissue Intestinal damage tissue enabling damage bacterial penetration Genetic Defect Bacterial Clearance Bacterial Infiltration of the Intestines + + Environment Unknown factors Defect of apoptosis of Activated T Cells Abnormal Stimulation regulation of the adaptive of the immune immune system system Tissue Intestinal damage tissue enabling damage bacterial penetration Decrease bacterial triggering through all 3 compartments ( refuges) Luminal Biofilm Intracellular Simultaneous apoptosis Decreases bacterial triggering through all 3 compartments ( refuges) Luminal Biofilm Intracellular Promotes prolonged apoptosis of activated T cells AIEC sensitive Reduces epithelial permeability by up regulating Claudins Occludins and JAM A All patients treated identically, all patients seen at week 0,4 and 8 weeks with PCDAI and CRP Weeks 0-4 Weeks 4-8 Primary end point remission ( PCDAI <7.5 without height or <10), variables associated with remission Secondary end point was normalization of CRP at week 8 ( <0.5 mg/dL) Azithromycin 7.5-10 mg /kg /day 5 days a week (max 500mg)+ Metronidazole 15-20 mg/kg daily (max 1000 mg) Azithromycin 7.5-10 mg /kg /day 3 days a week + Metronidazole 15-20 mg/kg daily Variable No Remiss P Value N=11 Total cohort N=32 Remission N=21 Baseline PCDAI 28 ± 10 25 ± 10 34 ± 6 P=0.004 Baseline CRP 3.2 ± 2.7 2.7 ± 2.9 4.2 ± 2.1 P=0.16 Baseline ESR 44 ± 19 44 ± 20 46 ± 17 NS Baseline albumin 3.8 ± 0.6 3.8 ± 0.6 3.7 ± 0.4 NS Baseline hemoglobin 11.3 ± 1.2 11.1 ± 1.2 11.7 ± 1 NS L1 Montreal 25% 29% 18% NS L2 22% 33% 0% NS L3 44% 33% 64% P=0.14 L4 41% 21% 64% P=0.07 L3+L4 13% 5% 27% P=0.11 (66%) (34%) PCDAI dropped from 28 ± 10 to 8.6 ± 8.3 (P<0.001) CRP declined from 3.2 ± 2.7 to 1.2 ± 2.6 mg/dL (P=0.04) ESR from 44 ± 19 to 26 ± 12 (P<0.001) CRP wk 8 normal 54% of patients with elevated CRP baseline We hypothesize that a 2-month antibiotic course of Azithromycin combined with Metronidazole is effective for inducing remission in active pediatric Crohns disease (CD). We also hypothesize that Azithromycin combined with Metronidazole is superior to the Metronidazole alone , and that remission will be accompanied by normalization of CRP in a high proportion of patients with active CD. Group 1: Group 2: Oral Metronidazole Oral Metronidazole + 10mg/kg X2/day (maximum 1000mg) for 8 weeks. 10mg/kgX2/day (maximum 1000mg day) for 8 weeks Oral Azithromycin 7.5 mg/kg once daily (maximum 500mg) 5 consecutive days a week for the first 4 weeks and 3 consecutive days a week for the last 4 weeks N=70 1. Children 5-17 years of age. 2. Diagnosis of active Crohn's Disease. 3. Patients with a PCDAI≥10 ≤40 (mild to moderate disease). 4. Have involvement of the colon and/or terminal ileum.. 5. The CRP ≥ 0.6 mg/dL. 6. Duration of disease since diagnosis < 3 years. Primary : Response rate at 8 weeks defined as a drop in PCDAI of at least 12.5 points (or remission without steroids, intention to treat principle) Secondary: 1. CS free remission rate at 8 weeks. 2. Normalization of CRP ( CRP ≤0.5 mg/dL) 3. Mean Fecal calprotectin at 8 weeks . 4. CS free remission at 12 weeks 1. 2. 3. Fecal samples for microbiome at baseline 8 and 12 weeks Does Microbiome predict response ? Is response dependent on changing microbiome? *Analysis of Microbiome from samples and Bioinformatics will be performed in Boston. Clinical ◦ Offer alternative therapy that does not require immune suppression ◦ Does treating upstream event ( trigger for inflammation) early in disease change natural history Translational ◦ Can we identify a component in the microbiome which is present before therapy, changes in responders? Sites in Boston, Edmonton, 6 sites in Europe and 4 in Israel