* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Republic Exam wo answers
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
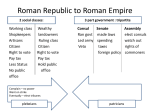
Roman Republic Exam ____ 1. According to legend, Romulus and Remus watched for a(n) ______ to decide where to build their city. (6.7.1) a. eclipse b. omen ____ ____ ____ ____ c. lightening bolt d. dark cloud 2. According to legend, who was the first king of Rome? (6.7.1) a. Remus c. Virgil b. Romulus d. Julius Caesar 3. The Roman Republic ended when ______________________. (6.7.2, 6.7.4) a. Spartacus lead a successful revolt c. the Plebeians left Rome for good b. Julius Caesar declared himself dictator 4. All of the following contributed to the success of Roman expansion except: (6.7.3) a. making allies of conquered people c. sharing wealth money with conquered people b. giving citizenship to some conquered d. maintaining strict military control over the people conquered people 5. The Romans built the city of Rome on seven hills which was on a broad, flat plane known as ______________. (6.7.1) a. latium b. palatine ____ c. nostrum d. aventine 6. Rome's early expansion involved taking over the Italian Peninsula and conquering the _____________________ who lived on the peninsula. (6.7.1) a. Greeks and Sicilians b. Greeks and Gauls ____ c. Gauls and Phoenicians d. Etruscans and Greeks 7. The second Punic War was unusual because the invading Carthaginian army used 60,000 men, 6,000 horses, and 37 _____________ to fight the Romans. (6.7.1) a. Giraffes b. Lions c. Elephants d. Bears 8. What was the first form of government in Rome? (6.7.1) a. Etruscan king c. dictatorship b. Roman Republic ____ 9. Why was the Twelve Tablets an important change for the Romans? (6.7.1) a. It ended debt bondage. c. It gave plebeians the right to vote. b. It created the first written laws. ____ 10. Which of the following is a difference between the geography of Rome and ancient ____ Greece? (6.7.1) a. b. c. d. Rome has a milder climate. Rome has more land for farming. Rome has better natural harbors. Rome has better access to trade routes. ____ 11. What northern mountain range separates the Italian peninsula from the rest of Europe? (6.7.1) a. Apennines b. Tiber c. Alps d. Himalayas ____ 12. The Patricians and the _____________ were the two main social classes in Rome. (6.7.1) a. patrons b. clients c. plebeians d. tribunes ____ 13. What was important about the creation of the Twelve Tables? (6.7.1) a. They ended debt bondage b. They were the first written laws in Roman history c. They gave plebeians the right to vote ____ 14. Why did many Romans make being a soldier a career? (6.7.3) a. Women could become soldiers. b. The government started paying the fighting men. c. Farmers were not allowed to work as soldiers. ____ 15. Rome fought the Punic Wars with which other country? (6.7.3) a. Macedonia c. Carthage b. Spain ____ 16. What did the Romans offer people who they conquered? (6.7.3) a. slavery c. banishment b. Roman citizenship ____ 17. What was the basis of the Roman economy? (6.7.3) a. weaving c. tourism b. farming d. mining ____ 18. Why was it possible for Roman cities to become centers of business and trade? (6.7.3) a. Roman citizens wre the only ones allowed to buy goods b. Only people living in cities could afford to buy trade items c. The network of paved roads allowed goods to move freely. ____ 19. Using the chart above, what can you tell about the Patricians and the Plebieans? (6.7.2) a. Plebieans had more power b. Each group became important in the running of the Roman government c. Only Patricians could be Consuls d. Patricians didn’t want to be in the Senate ____ 20. The Tribune of Plebieans was created ____________________________. (6.7.2) a. when the Plebieans protested and left the c. by Spartacus city of Rome b. to give the Plebieans a place in government other than the Senate d. by the Consuls to help get women involved in government ____ 21. The Plebeians left Rome because they ____________________. (6.7.2) a. wanted to protest the use of slave labor c. wanted more political power b. disagreed with Rome's military policies d. none of these choices ____ 22. The images above are of Fasces Sticks. These are symbols of government power the Romans took from the Etruscans. They represent the King’s power to ___________________. (6.7.1) a. buy and sell lumber for his cities b. rule in this life and the afterlife c. raise an army and conquer other lands d. detroy and rebuild his civilization ____ 23. The government of Rome began with which of the following? (6.7.1) a. Etruscan kings c. Great Dictator b. Roman Republic d. Res Publica