* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aptamer-targeted inhibition of mTOR in T cells enhances antitumor
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
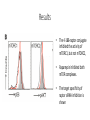
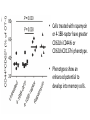
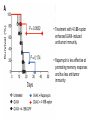
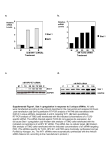
Aptamer-targeted inhibition of mTOR in T cells enhances antitumor immunity Alexey Berezhnoy, Iris Castro, Agata Levay, Thomas R. Malek, and Eli Gilboa J Clin Invest. 2014;124(1):188–197 Background (siRNA) • siRNA (small interfering RNA) - ability to inhibit target genes • Aptamer - oligonucleic acid molecules that bind to a target molecule. • Aptamer-siRNA conjugate - delivery vehicle composed of a targeting part (aptamer) and a therapeutic part (siRNA). Background (T Cells) • Memory T cells – T cells that have encountered and responded to their specific antigen. • They can recognize invaders and at a 2nd encounter can reproduce to mount a faster and stronger immune response than the 1st time. Background • Elevated levels of mTOR promote the accumulation of short-lived effectors rather than memory cells. • Pharmacological agents can have undesirable effects due to their broad range Aim of the study Aptamer-targeted siRNA inhibition of mTOR in CD8+ T cells enhances a vaccine-induced memory and an antitumor immunity that is superior to pharmacological treatment. Methods • siRNA specific to raptor (a component of mTORC1) • Aptamer that binds to 4-1BB, a molecule that is expressed on CD8+ T cells Test if siRNA inhibits mTORC1 activity. Test if mTOR inhibition causes formation of memory CD8+ T cell Test if siRNA can enhance vaccineinduced memory responses Methods • Goal: 4-1BB-raptor is capable of inhibiting mTOR activity • OT-I cells transferred into mice, and mice vaccinated with OVA peptide and then treated with: • rapamycin • 4-1BB aptamer-GFP siRNA (4-1BB-GFP) • 4-1BB aptamer-raptor siRNA (4-1BB-raptor) • mTORC activity measured Results • The 4-1BB-raptor conjugate inhibited the activity of mTORC1, but not mTORC2, • Rapamycin inhibited both mTOR complexes. • The target specificity of raptor siRNA inhibition is shown Methods • Goal: mTOR inhibition leads to the generation of enhanced memory CD8+ T cell responses • OT-I cells transferred into mice, mice vaccinated with OVA peptide and then treated with: • rapamycin • 4-1BB aptamer-GFP siRNA (4-1BB-GFP) • 4-1BB aptamer-raptor siRNA (4-1BB-raptor) • Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. • Cells treated with rapamycin or 4-1BB-raptor have greater CD62Lhi CD44hi or CD62LhiCD127hi phenotype. • Phenotypes show an enhanced potential to develop into memory cells. Methods • Goal: 4-1BB-raptor can enhance vaccine-induced memory responses • Mice were vaccinated with B16 melanoma cells (GVAX) and then treated with: • Rapamycin • 4-1BB aptamer-GFP siRNA conjugate (4-1BB-GFP) • 4-1BB aptamer-raptor siRNA conjugate (4-1BB-raptor) • Then, on day 50, the mice were challenged with parental B16 tumor cells and survival was determined Results • Treatment with 4-1BB-raptor enhanced GVAX-induced antitumor immunity. • Rapamycin is less effective at promoting memory responses and has less antitumor immunity Author’s Interpretation • siRNA inhibition of mTORC1 enhances vaccine-induced immunity. • Aptamer-targeted siRNA superior to rapamycin in terms of protective antitumor immunity in mice. • Rapamycin inhibits mTORC1 and mTORC2. Since mTORC2 is in cell survival, and glucose homeostasis, inhibition could be harmful • Cell targeting reduces dose of siRNA needed, reducing the risk of nonspecific immune activation Critique • Side-effects of inhibition of mTOR on other cellular processes was not examined • Enhancement of memory T-cells not directly measured • Mechanism of the immune response in the enhancement of antitumor immunity still needs to be investigated • 4-11B expression is upregulated on cells other than CD8+ so more specific targeting receptors will improve the specificity • Currently, only in mouse model, no human studies conducted so therapeutic applications not completely confirmed Questions?