* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download to create the Roman Empire
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
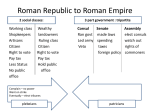
The Roman Empire Peninsula (surrounded by water on 3 sides) Only 120 miles across Apennine: Mountain range that runs north to south down the middle of Italy that divides it into east & west (did NOT isolate the cities like they did in Greece) Alps: mountains that border northern Italy Low lying fertile lands known as Plains (Po River Valley) Located 18 miles inland on the Tiber River Had access to the sea and also protection from pirates/invaders Built on 7 hills-easily defendable Central location in Italy Latins settled central Italy in the region of Latium (spoke Latin) with farming and herding settlements 753 B.C- Legend that Rome was founded by Romulus and Remus - Do you remember the story? The Greeks & Etruscans begin to settle Italy as colonies Culture is transferred to Italy/Rome Created the forum or marketplace in Rome Brick, stone & the arch Greek religious beliefs 7 Estruscan kings set up harsh rule & cruel gov’t 509 B.C: Romans revolt & drive out Etruscan’s Romans declare their city a Republic: officials chosen by the people, leader is NOT a monarch 509 B.C-27 B.C First 200 years Rome was in constant warfare with its neighbors Rome crushed Latin states, defeated Greeks & Estruscans 240 B.C.: Rome conquers almost all of Italy Roman Confederation: allowed conquered peoples citizenship & freedom of their own affairs if they supplied soldiers to Rome Sense of duty, courage & discipline Good diplomats but could be firm when needed Excelled in military matters/strategists They were practical Social Structure (2 groups) Patricians: wealthy landowners, ruling class, only citizens to hold political office Plebeians: non-aristocratic citizens, merchants, artisans, farmers & laborers All could vote but only Patricians could be elected to office Roman Senate: 300 elected Patricians who served for life & oversaw the government Consuls: chief executive officers elected every two years to run the government & lead the army. Had VETO power over the Senate Praetors: individuals in charge of civil law for citizens & non citizens Centuriate Assembly: a “peoples’ assembly” where elected consuls and praetors passed laws and was organized by social classes Conflict often broke out between plebeians and patricians over social & political inequality Plebeians eventually won the right to: Council of Plebs: created to give a voice to plebeians in the government & ability to pass laws Tribunes: elected representatives of the plebeians in the Senate Serve in public office & become consuls Marry patricians Twelve Tables: first code of laws, created to protect the rights of plebeians…..later developed into: Corpus Juris Civilis: civil laws that applied to all Roman citizens – legal questions Law of Nations: universal set of laws based on reason that applied justice to ALL people Innocent until proven guilty Able to defend yourself in front of a judge Roman expansion met conflict with the city-state of Carthage: extreme trading power of Mediterranean Carthage seized the Straits of Messina (waterway between mainland Italy & Sicily) and cut Romans off from the island Rome’s navy defeats Carthage navy in 241 B.C Rome forces Carthage to give up all rights to Sicily & made Carthage pay a fine for war damages Carthage general Hannibal invades Italy by crossing the Alps with 46,000 men & cavalry & 37 war elephants Romans met them head on at the Battle of Cannae: Romans lost almost 40,000 men Hannibal roams Italy but is unable to attack Rome due to low supplies & men Rome attacks Carthage troops and forces them out of Italy Roman troops defeat Hannibal’s army at the Battle of Zama in North Africa: gained Spain Rome is now dominant power in Mediterranean and looks to conquer Greece Rome completely destroys Carthage Survivors were sold into slavery and the territories of Carthage became the province of AFRICA By 146 B.C., Rome was the master of the Mediterranean world gaining control over Macedonia, Pergamum & Greece Section 2 Notes Wealthy landowning Senate held most of the power in the Government Aristocrats stripped land from small farmers Poor citizens began moving to the cities (Rome) Tiberius and Haius Gracchus: urged the Council of Plebs to propose land bills stripping aristocrats’ land & giving it to the poor; BOTH men murdered by Senate These actions angered many peasants 82-31 B.C. a series of civil wars occurred as individuals competed for political power Crassus- richest man in Rome Pompey- military hero Julius Caesar- military commander in Spain These 3 men formed the First Triumvirate Triumvirate: a government by 3 people with equal power Caesar take his troops into Gaul (France) and conquers it- gaining fame Crassus is killed in battle in Syria Senate decides to only have one leader – Pompey – and votes Caesar out Angry Caesar refuses to give up his power and illegally crosses the Rubicon River (northern boundary of home Roman lands) Caesar attacks Pompey’s troops and defeats them 45 B.C. : Caesar gains control of Rome and forces the Senate to name him “dictator for life.” Broke up lands of those disloyal to him and gave it to the poor Increase the size of the Senate to 900, weakening their power Granted citizenship to all who supported him as a leader Created building projects to generate jobs Adopted a new solar calendar (Julian Calendar) with 365 ½ days Many Senators believed Caesar wanted to become a king & had no anticipation of giving his power back to the Senate (DICTATOR) March 15th, 44 B.C.: group of Senators led by Marcus Brutus assassinated Caesar (IDES OF MARCH) Caesar’s Death Caesar’s Death Octavian (Caesar’s nephew & heir) Marc Antony (Caesar’s general) Marcus Lepidus (Caesar’s cavalry commander) A power struggle eventually breaks out b/w the three Lepidus retires & Antony & Octavian divide the Roman rule into two (Octavian west/Antony East) Antony & Octavian continually disagree & fight Antony allies himself with Egyptian queen Cleopatra & begins withholding grains from Rome Octavian convinces the Senate to go to war against Antony & Cleopatra 31 B.C.: Octavian smashes Antony’s forces at the Battle of Actium Both Antony & Cleopatra flee to Egypt where they both commit suicide Antony stabs himself first thinking that Cleopatra did the same (which she did not) After dying in her arms, Cleopatra is taken away but later commits suicide by allowing herself to be bit by a venemous snake. 32 years old and now becomes the supreme Ruler of Roman world 27 B.C. Octavian proclaims restoration of the Republic, made dictator for life and is given the name Augustus by the Senate Octavian moves to create the Roman Empire Polytheistic: Worshipped an official state religion of numerous Gods & Goddesses (combination with Greek Gods) Tolerant of other religions as long as they also worshipped Roman gods & emperors Romans sought a higher world of reality and promise of a future life superior to the present one 6 B.C.: old lands of Judah became the Roman territory of Judaea under the direction of a Roman official (procurator) Different groups had different opinions about Roman rule: Sadducees- priests who favored cooperation with Rome Pharisees- scholars who believed religious law protected them from Roman influences Essenes- waited for God to save Israel from Roman rule, lived apart from society Zealots- called for the violet overthrow of Roman rule A Jewish revolt was quickly crushed by Romans Jewish prophet named Jesus traveled across Judaea & Galilee preaching His mission was to complete the salvation God had promised to the people of Israel Believed God’s command was to love God and one another Taught ethical concepts of humility, charity & love Some thought Jesus was a revolutionary who threatened to overthrow Roman rule/influence Pontius Pilate: procurator who ordered Jesus arrested & crucified Followers of Jesus believed he had risen from the dead & that he was the Messiah (anointed one) that would save Israel Christianity spreads throughout the Empire Simon Peter: early apostle (leader) of Christianity, Jesus’ chief disciple Paul: most important apostle, founded Christian communities throughout eastern empire & taught Jesus was the Savior whose death made up for all the sins of humanity Apostles & Disciples wrote down the sayings of Jesus to form the Gospels- core of the New Testament By 100 A.D. Christian churches existed in all major cities in the eastern Roman Empire and spread to the west in 200 A.D. Romans initially viewed Christianity as another sect of Judaism Romans felt threatened b/c they refused to worship state gods/emperors Romans viewed refusal as treason- punishable by death Nero blamed Christians for problems in the empire and persecuted many Persecution continued for 200 years Reasons why Christianity grew so rapidly: It gave meaning & purpose to life, was personal, offered salvation & eternal life It was easy to relate to, Jesus was a human figure, didn’t require painful or expensive initiation rites Provided a sense of belonging among community Stressed spiritual equality to all classes of people Promised salvation to all First Roman emperor that converts to Christianity in 312 CE. Edict of Milan: creates official toleration of Christianity Council of Nicaea: organizes and unifies Christian doctrine Roman emperor who adopts Christianity as the official religion of the Roman Empire 380 CE Council of Thessalonica “A terrible rumor had arrived from the West. Rome is besieged…The City is taken which took the whole world. It had perished of famine before it died by the sword, and only a few captives were found…….An ancient and imperial city falls.” After the death of the last great Roman emperor, Rome experienced a period of civil war Severan Emperors: a new ruling family who attempted to halt the period of decline but were unable to hold onto power 235-284 A.D.: civil war broke out resulting in 22 emperors who ruled for short periods of time A series of plagues led to severe shortages in the labor force & military Decline in trade and food production Threats of invasions from Persians & Germans Emperor Constantine built a “New Rome” on the sit of the Greek city of Byzantium which became known as Constantinople Despite these efforts, high taxation & inflation could not be stopped Emperor Diocletian realized how big the empire was and the need for more effective ruling He divided the Roman empire into 2 parts (east & west) and created 4 tetrarchs (rulers) to rule 4 specific units Invasion of Germanic Tribes Rome was the capital in the West & Constantinople was the capital in the East Huns invade from Asia forcing the Germanic Visigoths & Vandals south and west into Roman territory 378 A.D.: Roman army is defeated by the Visigoths at the Battle of Adrianople 410 A.D. Visigoths becomes first Germanic people to sack Rome 455 A.D.: Vandals invade Italy and sack Rome 476 A.D.: Germanic leader Odoacer overthrows the last Roman emperor Romulus Augustus causing the official fall of the Roman empire in the West Rome falls….but what about the East??? The Eastern Roman empire will continue as the Byzantine Empire that will preserve Greek and Roman heritage. Christianity emphasis on spiritual kingdom weakened Roman virtues Roman valued declined as non-Italians gained importance in the empire Lead poisoning caused a mental decline in the population Plagues wiped out as much as 1/10 of the popluation Rome failed to advanced technologically because of dependence on slavery Rome couldn’t created a workable political system following the decline of emperors While all theories may have some sort of truth, there is still not one theory to explain the fall of the Roman empire