* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 9 Science – Unit 1 – Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
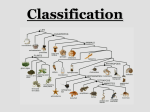
Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 1 Diversity How are species related? Section 1.2 – Pages 17-23 Classification needs to include morphology and phylogeny. This is accomplished with the concept of shared evolutionary history (i.e., organisms sharing an evolutionary history are related). Ancestor – An organism (or organisms) from which other groups or organisms are descended. Evidence of evolutionary ancestry is based on three types of evidence: (1) anatomical, (2) physiological and (3) DNA. This information is compared with the same information for other species and the evolutionary lineage is determined. Anatomical Evidence of Relationships Anatomy is the branch of biology that deals with structure and form, including internal systems. Recall, morphology refers to body size, shape and physical features to learn how an organism develops and functions structurally. Anatomy is a branch of morphology. See Figure 1.6 – Page 18 to learn how some dinosaurs and modern birds are anatomically related. As well, the two illustrations opposite some the foot of a Tyrannosaurus rex and a bird. Both have three forward toes and one toe facing back. As well, there are “claws” on all toes. Another comparison is the anatomical similarities among living species. As shown in Figure 1.7 – Page 18, four Animalia species – whale, bat, horse and human – have similar internal bone structures. The size of proportion of the bones have been modified by purpose (i.e., swimming, flying, running and grasping, respectively); yet, the arrangement and similarities suggest a common evolutionary history. Physiological Evidence of Relationships Physiology is the branch of biology dealing with the physical and chemical functions of organisms, including internal processes. Physiology includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells and biomolecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. By comparing these processes, the degree of genetic similarity can be assessed. DNA Evidence of Relationships Genes are section of DNA made of long chains of molecules called nucleotides. Sequencing of nucleotides is possible via gene mapping. Once a sequence is determined, it can be compared to the DNA of other organisms to assess similarities. As noted in Figure 1.10 on Page 20, DNA evidence has produced some surprising results. For example, fungi are more closely related to animals than plants. Phylogenetic Tree A branching diagram used to show the evolutionary relationships among species. Illustration show links between humans and apes (LCA = Last Common Ancestor) Task Compare the skeleton of a bird and a dinosaur Identify similarities which may link their evolutionary history.