* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction - Mr. hawkins
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
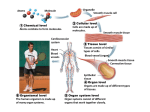
Introduction Anatomy and Physiology What is A&P • Anatomy – study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts • Physiology – study of how the body and its parts work or function • Gross anatomy • Microanatomy • Developmental Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. Cardiovascular system Heart Blood vessels 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Blood vessel (organ) Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems. 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely. Figure 1.1 Digestive system Takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and eliminates unabsorbed matter (feces) Respiratory system Takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide Food O2 CO2 Cardiovascular system Via the blood, distributes oxygen and nutrients to all body cells and delivers wastes and carbon dioxide to disposal organs Blood CO2 O2 Heart Nutrients Interstitial fluid Urinary system Eliminates nitrogenous wastes and excess ions Nutrients and wastes pass between blood and cells via the interstitial fluid Integumentary system Feces Protects the body as a whole Urine from the external environment Figure 1.2 Necessary Life Functions 1. Maintaining boundaries between internal and external environments 2. Movement (contractility) 3. Responsiveness: The ability to sense and respond to stimuli 4. Digestion 5. Metabolism: – Catabolism and anabolism 6. Excretion: The removal of wastes from metabolism and digestion 7. Reproduction 8. Growth Survival Needs 1. 2. 3. 4. Nutrients Oxygen Water Normal body temperature – Affects rate of chemical reactions 5. Appropriate atmospheric pressure Homeostasis • • • • • Maintenance of a stable internal environment a dynamic state of equilibrium Positive and Negative feedback Under constant change Neural and hormonal control systems – Receptor – Control center – Effector 3 Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor 4 Output: Control Center Afferent Efferent pathway pathway 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Information sent along efferent pathway to effector. Effector 5 Response of effector feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level. Figure 1.4 Control Center (thermoregulatory center in brain) Information sent along the afferent pathway to control center Receptors Temperature-sensitive cells in skin and brain Afferent pathway Efferent pathway BALANCE Stimulus Response Body temperature rises; stimulus ends Body temperature falls Effectors Skeletal muscles Shivering begins Effectors Sweat glands Sweat glands activated Response Evaporation of sweat Body temperature falls; stimulus ends Stimulus Body temperature rises Information sent along the efferent pathway to effectors Receptors Temperature-sensitive cells in skin and brain Efferent pathway Afferent pathway Information sent along the efferent pathway to effectors Control Center (thermoregulatory center in brain) Information sent along the afferent pathway to control center Figure 1.5 Body Cavities Serous Membranes • Line cavities and cover organs-linings are kept separate by the serous fluid secreted by these linings. • Visceral layer • Parietal layer Thoracic Membranes Abdominopelvic Membranes Visceral pleura Visceral peritoneum Parietal pleura Parietal peritoneum Visceral pericardium Parietal pericardium Organ Systems The Language of A&P • Special terminology is used to prevent misunderstanding • Exact terms are used for: – Position – Direction – Regions – Structures Body Sections Cranial cavity Cranial cavity (contains brain) Dorsal body cavity Dorsal body cavity Ventral body cavity Vertebral cavity Superior mediastinum Pleural cavity Pericardial cavity within the mediastinum Diaphragm Thoracic cavity (contains heart and lungs) Vertebral cavity (contains spinal cord) (a) Lateral view Ventral body cavity (thoracic and Abdomino- abdominopelvic pelvic cavities) cavity Abdominal cavity (contains digestive viscera) Pelvic cavity (contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum) (b) Anterior view Figure 1.9a-b Abdominopelvic Regions Abdominopelvic Quadrant Common Body Regions Time???? • Aging occurs at every level from organism down to molecular. • 3rd decade- begin to notice that joints stiffen, grey hair, fine lines and wrinkles…really old for women who want kids • 4th-5th decade- adult onset disorders like High BP, diabetes, heart disease, cancer ect…. • 6th decade-grayer and whiter hair, more and deeper wrinkles, vaccinations do not work as well • Loss of collagen, elastin, and subcutaneous fat cause wrinkles. • Cell reach end of predetermined cell divisions as telomeres wear away • Cell division is impaired so wound healing becomes a problem and cancer more likely • Have less mitochondria= less energy • Free radicals increase in number and destroy cellular organelles • Genetics will help us better understand • http://www.infoaging.org/