* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - PlanbookConnect
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
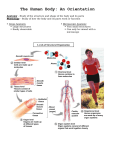
Biology II HP Chapter 1 EXAM Outline 50 Questions I. Introduction (basic functions of all living things) A. Responsiveness B. Growth C. Reproduction D. Movement E. Metabolism II. The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology(the study of internal & external structures, the study of functions) A. Microscopic Anatomy 1. Cytology-the study of cells & cell structures 2. Histology-the study of tissues, groups of cells with functional roles B. Gross Anatomy 1. Surface Anatomy-general & superficial markings 2. Regional Anatomy-superficial & internal features in a specific area of the body 3. Systemic Anatomy-structure of major organ systems C. Physiology 1. Cell Physiology-study of the living cell 2. Special Physiology-specific organs 3. System Physiology-all aspects of the function of specific organ systems 4. Pathological Physiology-studies the effects of diseases on an organ or organ system III. Levels of Organization A. Chemical or Molecular Level (atom/smallest level) B. Cellular Level (cell = individual living enity) C. Tissue Level (group of cells) D. Organ Level (group of tissues) E. Organ System Level (group of organs) ex heart & blood vessels, F. Organism Level (Living organism) IV. An Introduction to 11 Organ Systems (know function and major organs) A. Integumentary-protection from the environment, infection, hormone production, thermoregulation B. Skeletal-ligaments, support and protection C. Muscular-locomotion and heat production D. Nervous-electric signals to help regulate the body, response to stimuli E. Endocrine –Ex; thyroid gland, pituitary gland-directs long term changes F. Cardiovascular/circulatory-contains arteries, internal transport of materials G. Lymphoid-defense against infection H. Respiratory – trachea, lungs: delivery of air for gas exchange I. Digestive-processes food J. Urinary-urethra, elimination of excess water K. Reproductive-both male & female work together production of sex cells to produce a human organism V. Homeostasis and System Integration A. Homeostatic Regulation 1. Receptor-receives the stimulus 2. Integration Center (control center) receives and processes the stimulus 3. Effector-either opposes or enhances the stimulus B. Negative Feedback-corrective mechanism, opposes a variation of normal limits EX; C. Positive Feedback-reinforces the stimulus EX: D. Homeostasis and Disease- disease appears when failure of homeostatic regulation fails to occur VI. The Language of Anatomy (anatomical position) A. Surface Anatomy 1. Anatomical Landmarks Prone-face down Supine-face up 2. Anatomical Regions Abdominopelvic quadrant RUQ,LUQ RLQ,LLQ Abdominopelvic regions Cephalic-head Cervical-neck Thoracic-chest Abdominal-abdomen Pelvic-pelvis Lumbar-loin/lower back Gluteal-buttock Pubic-pubis Inguinal-groin Axillary-armpit Brachial-arm Manual-hand Femoral-thigh Cural-leg Sural-calf Pedal-foot Plantar-sole 3. Anatomical Directions “the wrist is DISTAL to the elbow” Anterior-front Ventral-belly side, front Posterior-back Dorsal-back Cranial-head Superior-above, higher level Caudial-tail Inferior-below, lower level Medial-toward longitudinal axis Lateral-away from the longitudinal axis Proximal-toward Distal-away Superficial-at, near, close to body surface Deep-farther from body surface B. Sectional Anatomy 1. Planes and Sections a. Transverse plane-right angle to long axis (superior & inferior) b. Frontal-along the long axis (anterior & posterior) c. Sagittal-runs along the long axis (mid & parasagittal) (right & left) 2. Body Cavities-protect internal organs and allow them to change shape. a. Dorsal Body Cavities-refers to the back 1. Cranial Cavity 2. Spinal Cavity b. Ventral Body Cavities 1. Thoracic Cavity Pericardial cavity 2. Abdominopelvic cavity-----separated by the diaphragm Abdominal cavity Pelvic cavity 4. Mediastinum (not a cavity, but a space) 5. Pleural Cavities-surrounds the lungs ***Know: The main function of the serous membrane Ventral Body Cavity=contains heart lungs and small intestine Histophysiology-studies function at the tissue level Visceral pleura-membrane covering the surface of the lung Appendicular –portion of the body that contains the upper and lower limbs