* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complement system
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
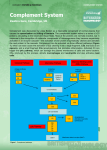
The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 - Complement system :is a protein cascade (like kinin and clotting factors)composed of more than 40 proteins including regulatory factors - Cascade is when one reaction triggers another reaction which trigger others and so on. These types of systems can grow exponentially very fast. -The components are made in the liver ,through some local production at sites of inflammation may be undertaken by macrophages -The complement system has 3 pathway ,which are all capable of igniting the another pathway ,known as the common or membranes attack pathway. -The majority of complement protein are soluble ,although some are membranes bound. 1 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 -The soluble protein circulate in an inactive state ,and each must be activated sequentially for the reaction to proceed. -The overall serum concentration of complement protein is 3-4µg\l i.e. around 10% of serum proteins. - Complement proteins are often designated by an uppercase letter C and are inactive until they are split into products. Example: C1 - When the products are split they become active. The active products are usually designated with a lower case a or b. Example: C1a and C1b -several biological activities appear as a consequence of complement activation ,the main ones being -1-Cell or bacterial lysis . 2-production of proinflammatery mediators ,which amplify and perpetuate the process. 3-Solubilisation of antigen-antibody complex. *The complement pathways. A-The classical pathways 1-is activated by an interaction between antigen and antibody forming so –called immune complex . 2 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 2-Antibodies can bind to, or fix complement only after reacting with their antigen . 3-The formation of the complex provokes a conformational change in the antibodies molecules that discloses a site for binding of the first complement component C1. 4-IN addition to antigen –antibody complexes ,the activation of the classical pathway can be initiated by aggregated immunoglobulin and by non-immunological stimuli such as C-reactive protein. Notes: • The classical pathway is considered to be part of the specific immune response because it relies on antibodies to initiate it. • C1 becomes activated when it binds to the ends of antibodies • • • • • Once C1 is activated, it activates 2 other complement proteins, C2 and C4 by cutting them in half C2 is cleaved into C2a and C2b C4 is cleaved into C4a and C4b Both C2b and C4b bind together on the surface of the bacteria C2a and C4a diffuse away 3 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 C3 Activation complex • C2b and C4b bind together on the surface to form a C3 activation complex • The function of the C3 activation complex is to activate C3 proteins. – This is done by cleaving C3 into C3a and C3b 4 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 -C3b • Many C3b molecules are produced by the C3 activation complex. • The C3b bind to and coat the surface of the bacteria. • C3b is an opsonin • Opsonin are molecules that bind both to bacteria and phagocytes • Opsonization increases phagocytosis by 1,000 fold. -C3a C3a increases the inflammatory response by binding to mast cells and causing them to release histamine The C5 activation complex -The C5 activation complex (C2b, C4b, C3b) activates C5 proteins by cleaving them into C5a and C5b -Many C5b proteins are produced by the C5 activation complex. These C5b begin to coat the surface of the bacteria The function of C5a • C5a disperses away from the bacteria. 5 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 – Binds to mast cells and increases inflammation. – Most powerful chemotactic factor known for leukocytes Building the Membrane Attack complex • • • • C5b on the surface of bacteria binds to C6 The binding of C6 to C5b activates C6 so that it can bind to C7 C7 binds to C8 which in turn binds to many C9’s Together these proteins form a circular complex called the Membrane attack complex (MAC) Membrane Attack complex • The MAC causes Cytolysis. – The circular membrane attack complex acts as a channel in which cytoplasm can rush out of and water rushes in. • The cells inner integrity is compromised and it dies • Animation of the classical pathway 6 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 The alternative pathway • The alternative pathway is part of the non-specific defense because it does not need antibodies to initiate the pathway. • The alternative pathway is slower than the Classical pathway • Availability of C3b is the essential requirement for activation of the alternative pathway to proceed ,this requirement is again fulfilled by the internal thioester bond ,which undergo continues low grade hydrolysis. • It is thought that bacteria provide a surface for C3b and C3bBp deposition and protection from the destruction action of circulating regulatory factors I and H. • The alternative pathway is slower than the Classical pathway. • The Alternative complement pathway 7 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 Initiation of The Alternative pathway • C3 contains in unstable thioester bond. • This unstable bond makesC3 subject to slow spontaneous hydrolysis to C3b and C3a • The C3b is able to bind to foreign surface antigens. • Mammalian cells contain sialic acid which inactivates C3b. • C3b on the surface of a foreign cells binds to another plasma protein called factor B • The binding of C3b to factor B allows a protein enzyme called Factor D to cleave Factor B to Ba and Bb. . Factor Bb remains bound to C3b while Ba and Factor D disperse 8 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 The C3 activation complex • Properdin, also called factor P, binds to the C3bBb complex to stabilize it. • C3bBbP make up the C3 activation complex for the alternative pathway • The C3 activation complex causes the production of more C3b. • This allows the initial steps of this pathway to be repeated and amplified • 2X106 molecules can be generated in 5 minutes C5 activation complex -When an additional C3b binds to the C3 activation complex it converts it into a C5 activation complex. -The C5 activation complex cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b. -C5b begins the production of the MAC. 9 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 Overview C-The LECTIN pathway or Mannan –binding lectin pathways. -Lectins are proteins which bind to carbohydrates -Many bacteria have many mannose residues on their surface. the lectin-based complement system begins with a “mannosebinding protein” (MBP). -MBP reacts, in turn, with a MBP-associated serine protease (MASP -MASP functions, in effect, like activated C1q[r2s2], that is a C3 convertase. D-The membranes attack pathway. -1-This final common complement pathway ,generate one of the more biologically active component ,C5a ,but more 10 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 importantly leads to the formation of the killer molecules of the system . 2-This is known as the membranes attack complex (MAC) since it provokes membranes damage. 3-MAC is composed of C5b6789 ,this complex is inserting into and traversing the membrane bilayer .Holes are made in the membranes ,and if a sufficient number are created death result through osmotic lysis . 4-Control is achieved by the liability of the component ,by dilution and by specific regulatory protein and receptors. *Biological activities generated by complement activities . 1-Opsonisation:The concept of Opsonization is that opsonin coat bacteria and this facilitate their removal one of the major opsonins derives from complement the ability to bind membranes is a feature of varies complement fragment ,but C3b account for the most of the complement opsonic activities ,once the organism are coated with C3b ,it is simple to see how the presence of CRs 3 and 4 on neutrophil can result in more efficient engulfment . 2-Cell recruitment and activation -The low –molecular weight fragment C4a,C5a are known as anaphylatoxin ,in which they activate mast cells and basophil directly through specific receptors . -C5a and to a lesser extent ,C3a are also chemoatactic ,a term used to describe the ability to attract cells ,in this case neutrophil. 3-Cell lysis :Complete complement activation through either pathway occurring on cell surfaces leads to cell lysis. -typical target could include bacteria and enveloped viruses ,but host erythrocytes ,platelet and lymphocyte may also become victims in certain pathological condition . 4-Removal of immune complex : -immune complexes of antibodies and antigen are forming in the circulation continuously in small number ,with periodic increase during infection or inflammatory episodes 11 The complement system immune system 2nd class NO.2 -These are potentially harmful ,since they can become deposited in vessel walls or tissue and initiate complement activation with all the pro-inflammatory effect that are entail -Larger complexes ,composed of lattice of antibodies and antigen are more likely to become insoluble and fixed in the tissue . -The covalent binding of C3b to antibodies in a complex inhibit lattice formation and maintains solubility . -C3b –coated complexes attach to erythrocyte CR1 ,which act to remove them from circulation via the liver and spleen where they are released and taken up by resident macrophages. 12