* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome To My Presentation Of *Perception
Personal identity wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
First impression (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Attribution bias wikipedia , lookup
Impression management wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
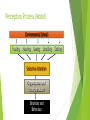
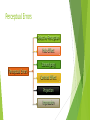
Welcome To My Presentation Of *PERCEPTION* By Pra-YasH New-Pane Introduction Perception is one of the important cognitive factors of individual Behaviours. Perception is a process by which an individual selects, organizes and interprets stimuli into a meaningful picture of the environment. Differs from one person to another depending upon needs, values and expectation. People respond to situations on the basis of their perception about the reality rather than reality itself. Nature/Feature of Perception Base of every individual’s Behaviour. Psychological/cognitive process. Differs from person to person and situation to situation. Not always based on reality. Directly related to motivation and personality. Can be developed. Perception Process (Model) Environmental Stimuli Feeling Hearing Seeing Smelling Selective Attention Organization and Interpretation Emotions and Behaviour Tasting INPUTS Perceived inputs are the objectives, events, people etc. They are received by the perceiver. It begins when environmental stimuli are received through our five sense organs. Five sense organs are Eye(Seeing), Ear(Hearing), Skin(Feeling), Nose (Smelling), Toung(Tasting). PROCESSES The inputs received through sense organs are processed through the three subprocesses. Selection : The process of filtering information received by our sense organ is called selective perception. The selective perception involves two psychological principles: a) Figure – Ground principle b) Relevancy principle Organization: Perceptual organization is the process by which we group selected information. a) Grouping b) Closure (Bridging the gap) c) Simplification Interpretation: It is highly subjective and judgmental in nature which is influenced by many factors and without it perceive information would be meaningless. OUTPUTS The output of perception can be seen in the form of Behaviours and emotion. They can be feelings, actions, attitudes etc. Perceptual Errors Selective Perception Halo Effect Stereotyping Perceptual Errors Contrast Effect Projection Impression Contd. Selective Perception: People selectively interpret what they see on the basis of their interest, background, experiences and attitudes. Halo Effect: It refers to the tendency of judging person entirely on the basis of a single trait which may be favorable or unfavorable. Stereotyping: It means classifying people and event into already known general categories or groups. Contrast Effect: It occurs when we evaluate a person’s characteristics that are affect by the comparison with other people. Projection: It refers to the tendency of the people to see their own trails in other people. Impression: We frequently from impression of others on the first sight. ( First impression is the last impression ) Principle of Perpetual Selection Intensity: More intense the stimulus, the more likely it is to be Size: Larger an external factor, the more likely it is to be perceived and vice Contrast: The external stimuli that stand out against the background or that are not what people are expecting will perceive more attention. Repetition: The Repeated external stimulus is more attention getting than a single one. Motion: People will pay more attention to moving objects in their field of vision. Novelty: Either a familiar or a new factor in environment can attract more attention. perceived. versa. Social Perception Social perception is directly concerned with how one individual perceives other individuals. To learn about other people, they rely on information from their physical appearance, and verbal and nonverbal communication There can be ways in which people communicate without words— including through facial expressions, tone of voice, gestures, body position and movement, touch, and gaze. A different perceptual activity ,called the attribution process (theory), help us to interpret the world around us. Attribution Theory When people attach cause and effect explanation to their Behaviour, it is known as attribution. “Attribution theory deals with how the social perceiver uses information to explain events. It examines what information is gathered and how it is combined to form a causal judgment” (Fiske & Taylor, 1991) Perception of a person depends to a large extent on whether he attributes the observed Behaviour. The Attribution Process Antecedents Factors internal to the perceiver Attributes Information Beliefs Motivation Perceived causes of Behaviour (such as internal vs. external causes) Made by the perceiver Consequences For the perceiver Behaviour Feeling Expectations Internal vs. External Causes of Behaviour Consistency: This is related with the repetition of the same kind of behaviour. It is the extent to which the person perceived behaves in the manner on other occasions when faced with the same situation. Distinctiveness: It refers to the extent to which the same person behaves in the same fashion in different situation. They are those that are relatively unique to the situation. Consensus: It is the extent to which other people in the same situation behave in the same way as the person under observation. Factors Influencing Perception Feedbacksssss?????????????????