* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ocean basins
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
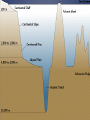
OCEAN BASINS Grade 8 Science 2012 OCEAN BASINS Oceans form the largest ecosystem on Earth. Much remains to be discovered about what lies below the ocean’s surface. Only about 1% of the ocean floor has been mapped Most of the ocean (100 metres and below) is pitch-black. Continental Shelf – the gradual slope between the coastline and the edge of the ocean basin Continental Slope – a steep drop dividing the continental slope and the ocean basin Abyssal Plain – wide, open, flat plains that stretch out along the ocean basin Oceanic Trench – narrow, deep, and steep sided canyons running along some ocean floors. Some of the deepest places on Earth A JOURNEY ON THE OCEAN FLOOR The and formation of the ocean landscape are due mainly to the movements of Earth’s tectonic plates. Features in the ocean basins are much bigger than on land. There are mountain ranges taller than the Himalayas. Steep valleys deeper than the Grand Canyon. Plains wider than the Canadian Prairies. CONTINENTAL SHELVES & SLOPES Ocean basins do not begin at the coastline. They begin may km out at sea. The area between the coast and the edge of the ocean basin is actually a submerged part of the continent, called the continental shelf. Continental Slopes exist at the edge of the shelves and plunge at steep angles to the sea floor. SEAMOUNTS Large underwater mountain peaks called seamounts exist at the edges of midocean ranges. Seamounts are most often found in clusters and are most common in the Pacific Ocean. TRENCHES Along the sea floor are narrow, steep-sided canyons, called trenches. They are formed where the edge of an ocean plate pushes against the edge of a continental plate. As the plates move together, the ocean plate is forced to bend steeply down beneath the heavier continental plate. TRENCHES (CONT.) The deepest trench, Marianas Trench, extends 11 km below sea level. Nearly SEVEN times deeper than the Grand Canyon and deep enough to submerge an object as tall as Mount Everest. ABYSSAL PLAINS Between the high mountains and the deep trenches, the ocean floors are very flat. These wide open features are called abyssal plains. They are formed of thick deposits of sediment, up to 1 km deep in places. As tectonic plates move apart or together, some oceans expand, while other shrink. Precise measurements show that the Atlantic Ocean is expanding, carrying North America and Europe farther part at a rate of 3 cm per year. MID-OCEAN RIDGES Long undersea mountain chains called mid-ocean ridges run along the ocean floor These ridges are the youngest areas of the sea floor and are still being formed by volcanic eruptions. Molten lava flows from these ridges, quickly hardening into new plate material that pushes tectonic plates further apart. Mid-ocean ridges are more than 1000 km wide and rise over 10003000 m above the sea floor. VIDEOS MAPPING OUT THE OCEAN FLOOR Please get a textbook and open to page 361.