* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
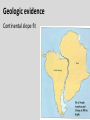
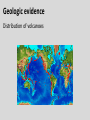
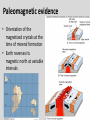
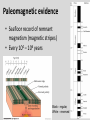
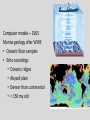
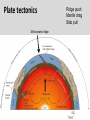
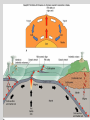
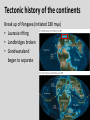
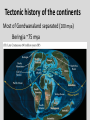
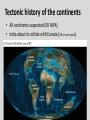
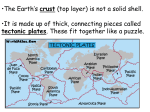
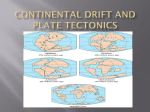
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Age of Earth estimates through time Linnaeus Wallace Modern radioactive dating Half life Oldest fossil Photoautotrophic prokaryote from Australia/South Africa (~3.5 bill yrs BP) Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) • Proposed the theory of continental drift in early 1900’s • Who’s original idea? • Antonio Snider-Pelligrini (1858) • Mechanism not explained Evidence • • • • • Geologic Stratigraphic Paleoclimatic Paleontological Paleomagnetic Geologic evidence Continental slope fit Geologic evidence Distribution of earthquakes Geologic evidence Distribution of volcanoes Geologic evidence Mountain ranges Stratigraphic evidence Matching sequence of rock strata on different continents Precambrian shields Flood Basalts Paleoclimatic evidence • Glacial deposits • Scouring on rocks indicate the direction Paleoclimatic evidence Paleontological evidence Glossopteris fossil record Paleontological evidence Mesosaurus fossil record Paleomagnetic evidence • Orientation of the magnetized crystals at the time of mineral formation • Earth reverses its magnetic north at variable intervals Paleomagnetic evidence • Seafloor record of remnant magnetism (magnetic stripes) • Every 104 – 106 years Black - regular, White – reversed Computer models – 1965 Marine geology after WWII • Oceanic floor samples • Echo soundings • Oceanic ridges • Abysall plain • Denser than continental • < 150 my old Continental Drift – continents were once united and have since become independent structures that have been displaced all over the globe Plate Tectonics – study of the origin, movement and destruction of plates and how these events have been involved in the evolution of Earth’s crust Plate tectonics Crust Continental (felsic) Oceanic (mafic) Mantle Lower lithosphere Asthenosphere Outer Core Inner Core Why is continental crust generally much older than the current oceanic crust? Plate tectonics Mid-oceanic ridge Ridge push Mantle drag Slab pull Plate tectonics 19 major tectonic plates Plate Boundaries Divergent boundaries Convergent boundaries Transform boundaries Tectonic history of the continents Reconstruction of tectonic history • Paleomagnetic declinations • Symmetrical magnetic stripes • Topographic and bathymetric maps • Lithologic indicators of climate Tectonic history of the continents Pangaea: ancient supercontinent (~250 mya) Tectonic history of the continents Break up of Pangaea (initiated 180 mya) • Laurasia rifting • Landbridges broken • Gondwanaland began to separate Tectonic history of the continents Most of Gondwanaland separated (100 mya) Beringia ~75 mya Tectonic history of the continents Most of Gondwanaland separated (100 mya) Landbridges btwn Europe and NA Tectonic history of the continents • All continents separated (50 MYA) • India about to collide with Eurasia (20 cm per year!) Tectonic history of the continents Central American Landbridge ~3 mya Great American Interchange Formation of Isthmus of Panama – 3 MYA North American ungulates, proboscids, carnivorans, rodents dispersed south South American ground sloths and terror birds, armadillos dispersed north