* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANT CELLS and TISSUES
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
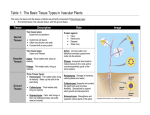
Objective: I will be able to know and understand the meristematic tissues and permanent tissues of a plant by completing a collage. PLANT CELLS PLANT TISSUES CELLS that work with other cells for a COMMON FUNCTION TISSUES MERISTEMATIC Apical Lateral PERMANENT Interecalary SIMPLE COMPLEX Parenchyma Vascular Collenchyma Xylem Schlerenchyma Phloem DERMAL Epidermis Cork & Cork Cambium MERISTEMATIC vs. PERMANENT TISSUE Meristematic Permanent Undifferentiated cells undergoing active Cells where growth and growth Mitosis- cells dividing differentiation is complete. MERISTEMATIC TISSUESAPICAL Growth in length Primary growth Root and shoot tips MERISTEMATIC TISSUESLATERAL Growth in width or girth Secondary growth Vascular cambium- dicots only MERISTEMATIC TISSUESINTERCALARY Growth from the base of nodes Grasses Allows grass to be cut short and still grow PERMANENT TISSUES- SIMPLE Contain only one type of cell Parenchyma Large rounded, loosely packed cells Primary in cell wall Produce and store food or compounds like nectar and latex Collenchyma Elongated, unevenly thickened walls Adds strength but flexible Supports young organs (leaves, stem, and roots) Sclerenchyma Elongated cells in secondary cell wall Thickest, most rigid cell walls DEAD Conducts, supports, and protects PERMANENT TISSUESCOMPLEX Two or more different types of cells VASCULAR tissues XYLEM – conducts WATER PHLOEM – conducts FOOD DERMAL tissues EPIDERMIS – single cell layer CORK & CORK CAMBIUM PERMANENT TISSUES – Complex Vascular PHLOEM – conducts FOOD Sieve tubes Elongated cells with sieve plates on ends, cytoplasm flows from cell to cell, living with no nucleus Companion cells Contains nucleus and controls activity of both cells XYLEM – conducts WATER Vessels Shorter, much wider cells that lack end-plates Tracheids Long and tapered with angled end-plates, in more primitive plants PERMANENT TISSUES – Complex Dermal EPIDERMIS protection from water loss, heat, insects and diseases GAS EXCHANGE Cuticle Waxy layer on epidermis for protection Guard cells and stomata Opening on bottom of leaf Trichomes Outgrowth of epidermal cells to form hairs or glands PERMANENT TISSUES – Complex Dermal CORK & CORK CAMBIUM Outer bark of woody plants Protects from water loss, insects, and diseases Closely packed cells for protections Suberin to repel water Assignment Plant tissue assignment sheet