* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
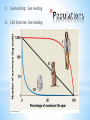
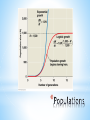
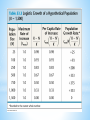
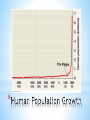
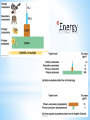
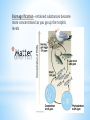
* Ecology and Biosphere *Study of the interactions of organisms with each other and their environment * *Biotic-living *Abiotic- non-living Biotic Biotic * Abiotic Abiotic * Population-group of organisms of same species in a specific area * Community- all the populations in an area * Ecosystem- community + abiotic factors * Biome- Major ecosystem that occupies a broad geographic region influenced by climate and characterized by dominant vegetation * Biosphere- all portions of Earth inhabited by life / all of Earth’s ecosystems * * *Determined by… *sunlight, *temperature, *water, *wind, *elevation * * * * A. Interactions 1. * Competition—usually for resources Niche—organism’s role in its environment ~Can’t have 2 species with the same niche in the same area because of the Competitive Exclusion Principle—2 extremely similar species cannot co-exist in the same place because one will be slightly better at getting the resources and reproduce more. * Resource Partitioning—resources are divided so that species can co-exist and each have it’s own niche * 2. Predation * * Animalanimal = predator / prey Animalplant = herbivory 3. Symbiosis * * * Mutualism (+,+) Parasitism (+,-) Commensalism (+, 0) * B. Trophic Structures * Food web—Messy = Stable * 2. Length of Food Chain in Food Web * Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) * Dynamic Stability—shorter chains are more stable because disruptions are magnified as you go up (the lower you wipe something out, the more effect it has) * C. Community Stability 1. Dominant Species—highest in terms of biomass (usually a plant) 2. Keystone Species—not most abundant but most important due to ecological role. If it’s removed from ecosystem there’s a major effect 3. Succession—Predictable sequence of communities that follow each other after a disturbance * * Succession Terms * Disturbance—what originally “damages” ecosystem * Primary Succession—start with a virtually lifeless area * Secondary Succession—start with some biomass left * Pioneer Species—first species to come into an area * Climax Community—end stage / stable / due to climate * * A. Density: # of organisms/area * Quantitative * * 2 lions per mile2 Qualitative * The density of lions in my backyard is sparse. B. Distribution: How organisms are arranged/placed * Determined by resources and social behavior * * C. Survivorship: See reading D. Life histories: See reading * D. Population Growth * Variables: dY = amount of change dt = change in time B = number of births D = number of deaths N = population size K = carrying capacity rmax = maximum per capita growth rate of population b = per capita birth rate m = per capita death rate Population Growth: dN = B – D OR dN = bN - mN dt dt * * * * * Density Dependent Factors: Population limiting factors whose effect depends on population density Density Independent Factors: Population limiting factors that are not dependent on population density * * * A. Productivity—turning light into sugars 1. Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)—amount of light energy converted to chemical energy in photosynthesis over time 2. Net Primary Productivity— (amount of GPP) – (energy used by plant in cellular respiration [R]) NPP = GPP – R 3. Limits on Production—sun (intensity, depth, penetration); limits on photosynthesis (water); limiting nutrients (N & P) * Net Annual Primary Production vs. Mean Annual Precipitation * B. Ecological Pyramids (See Pictures) 1. Production / Energy—amount of energy stored at each level 2. Biomass—amount of biological mass at each level 3. Numbers—number of organisms at each level * * * * * * * * Biomagnification—retained substances become more concentrated as you go up the trophic levels * C. Greenhouse Effect—Carbon Dioxide (and other gases) allow light through but trap the heat it generates in the atmosphere Global Warming—due to increased carbon dioxide levels, causing increased greenhouse effect *