* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 22-23-Effector T-cells-Th-Tc
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
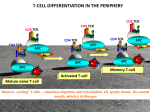
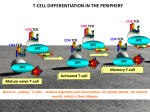
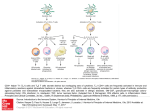
T-CELL DIFFERENTIATION IN THE PERIPHERY CD8 TCR CD8 TCR CD8 TCR CD4 TCR CD4 TCR CD4 TCR APC APC APC Ag Ag Ag APC APC APC Memory T-cell Activated T-cell Mature naive T-cell Naive or „resting” T cells… restless migration and recirculation, LN, lymph, blood…for several month, which is their lifespan PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE IMMUNE RESPONSES ARE NOT INITIATED IN THE PERIPHERY Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antigen presenting cells are not activated in normal tissues NO SIGNAL 3. for CD4+ Th activation PERIPHERAL TISSUES TOLERIZE THEMSELVES T-CELL DIFFERENTIATION Environmental factors and interactions with APCs initiate distinct differentiation programs in naive T-cells Arming of effector T cells Clonal selection and differentiation APC T Activation of NAÏVE T cells by signal 1 and 2 is not sufficient to trigger effector function, but….. the T cell will be activated to proliferate and differentiate under the control of autocrine IL-2 to an effector T cell. These T cells are ARMED IL-2 Effector T cell How can this cell give help to or kill cells that express low levels of B7 family costimulators? Effector function or Anergy? Clonally selected, proliferating and differentiated T cell sees antigen on a B7 negative epithelial cell The effector programme of the T cell is activated without costimulation Armed Effector T cell Armed Effector T cell IL-2 This contrasts the situation with naïve T cells, which are anergised without costimulation Naïve T cell CD28 TcR Co-receptor Kill Epithelial cell Epithelial cell Epithelial cell IL-12 FAVORS POLARIZATION TO TH1-TYPE EFFECTOR T-CELLS Virus, bacteria, protozoa, fungi NK cell IL-12 IFNγ Th1 IL-2 IFNγ TNF-β GM-CSF IL-3 DC MΦ CD8+ cytotoxic T cell IL-12 IFNγ IL-12 Th0 Th2 IL-4 IL-5 IL-10 IL-13 IL-10 FAVORS POLARIZATION TO Th2 Self tissue, tumor cell Macrophage DC Th1 IL-2 IFNγ TNF-β TNF-α GM-CSF IL-3 IL-10 Th0 IL-10 Th2 IL-4 IL-5 IL-10 IL-13 TOLERANCE POLARIZATION OF HELPER T LYMPHOCYTES IS DIRECTED BY DENDRITIC CELL-DERIVED AND AUTOCRINE CYTOKINES AND TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF TH1 CELLS Activation Killing Proliferation Feed back Entry to tissue Recruitment Granulomas develop when intracellular pathogens resist elimination Long term persistance of infectious agent in a separated envitonment Responses to Mycobacterium leprae are sharply differentiated in tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. EFFECTOR CD4+ HELPER T LYMPHOCYTES SECRETE DIFFERENT CYTOKINES Th1 Th0 IFNγ Th2 IL-4 IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 IFNγ, IL-2, TNF-β/LT Inflammatory cytokines Anti-inflammatory cytokines CELLULAR IMMUNE RESPONSE HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE SUBSETS OF HELPER T LYMPHOCYTES COLLABORATE WITH DIFFERENT PROFESSIONAL ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS B7 expression antigen presentation Germinal center formation Th2 CD40L CD40 B Affinity maturation Isotype switch IL - 4 Th1 CD40L IFNγ CD40 Memory B cell generation DC MΦ B7 expression antigen presentation MHC-II expression antigen presentation Mature dendritic cell Activated macrophage Th1 EFFECTOR HELPER T-CELLS CD4 TCR CD4 Naive CD4+ T cell TCR CD4 CD4 TCR TCR DC INTERACTION ACTIVATION INSTRUCTION CD4 TCR Th0 blast CD4 TCR CLONAL EXPANSION DIFFERENTIATION Intracellular pathogens Inflammation Tc activation IgG1 & IgG3 antibodies ADCC, opsonisation Complement activation Th2 Extracellular pathogens Multicellular parasites Secretory IgA IgE, allergy Th17 Extracellular pathogen Inflammation Autoimmune diseases Allergy Treg Th1 inhibition Maintenance of immunological tolerance EPIGENETIC CHANGES, MEMORY CHARACTERISTICS OF EFFECTOR HELPER T LYMPHOCYTES CCR1 CCR5 CXCR3 Th1 T-bet CCR6 CD45RBlo IL-12Rα LAG3 Th17 IL-23R RORγt TCR+ CD4+ CD28+ CD25+ CD25 IL-2Rα CD127 IL-7Rα↓ CCR4 CCR3 CXCR4 Th2 GATA3 Treg CD45RBhigh FoxP3 IL-1R CD30 GITR CTLA4 B7 ligand HOWEVER, THIS IS NOT THE END OF THE STORY… AS OF YET… CHARACTERISTICS OF EFFECTOR HELPER T LYMPHOCYTES – Th9 CELLS IL-2Rγ Th9 TCR+ CD4+ CD28+ CD25+ IL-4Rα PU.1 & IRF4 Th0 TGF-β IL-4 Th9 IL-9 IL-10 CCL17 CCL22 Parasitic helminth infections Chronic allergic inflammation Asthma Autoimmune diseases Other cytokines that enhance Th9 polarization: Type I IFNs , IL-1β, IL-6 Annunziato and Romagnani (2009) Arthritis Research & Therapy 11:257 Neurath MF and Finotto S (2011) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 22:83-89. Th2 functions Th2 cells stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of naive B cells ISOTYPE SWITCH IN ACTIVATED B CELLS IS REGULATED BY HELPER T CELL - DERIVED CYTOKINES ISOTYPE SWITCH IS INFLUENCED BY site of antigen entry tissue microenvironment nature of professional antigen presenting cells polarization of helper T lymphocytes REGULATION OF ISOTYPE SWITCH OF B CELLS IL-2 IL-4 IL-5 Helper T cell IL-2 IL-4 IL-5 IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IFNγ IL-5 TGFβ IgM IgG IgA B cell IL-4 B cell proliferation and differentiation – isotype switch IgE Human Ig classes and subclasses Complement activation Classical FcR binding IgM ++++ - IgG1 ++++ +++ IgG2 + + IgG3 +++ ++++ IgG4 +/- + IgA - +++ IgE - +++ IgD - - Cytotoxic T-cells PRIMING OF CD8+ CYTOTOXIC T CELLS PRIMING OF CD8+ CYTOTOXIC T CELLS THROUGH COLLABORATION OF HELPER AND CYTOTOXIC T-CELLS ACTIVATION CD40L CD40 APC CD4+ Th IL-2 B7 MHC I CD28 CD8+ Tc 1. Dendritic cells with high B7 expression activate CD8+ T cells directly 2. Dendritic cells activate CD4+ T cells, which in turn enhance the costimulatory activity of dendritic cells 3. Activated CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines (IL-2), which directly acts on activated CD8+ T cell KILLING OF INFECTED CELLS BY CTL Recognition by CTLs induces secretion of cytotoxins to the target cell PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PATHOLOGIC CELL DEATH Apoptotic signal Cell demage Apoptosis Necrosis DNS-ladder Inflammatory cytokines IL-1 TNFa IL-6 Macropha ge Granulocyte, macrophage APOPTOSIS AND NECROSIS Healthy cell Necrotic cell Late apoptotic cell Apoptotic cell HIGHLY REGULATED PROCESS 1. Induction 2. Excecution • Mitochondrial function * Activation of caspases • Electron transport * Serine protease,calpain, proteasome • Oxidative phosphorylateion * Redox potential • ATP synthesis * DNA degradation (endonuclease) MECHANISM OF CELLULAR KILLING BY CD8+ CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES H2O, Ca++, ions Proteoglycans Polymerized perforin Granzyme CYTOKINE RELEASE CD8 APOPTOSIS TCR MHC+ peptide ICE/CASPASE Crosslinking FasL Fas CD8+ T CELL TARGET CELL TNF AND TNF RECEPTOR FAMILY MEMBERS AND THEIR LIGANDS TNFRI Soluble TNF TNF-α TNFRII TNF-β/LTα LTβR LTβ LTα LTβ RECEPTOR TRIMERIZATION FAS DEATH DOMAIN Soluble FasL FasL CD40 CD40L CD30 CD30L CD27 CD27L 4-1BB 4-1BBL Ox40 Ox40L MECHANISMS OF FAS RECEPTOR – MEDIATED PROGRAMED CELL DEATH TNFRI trimerization Fas trimerization TNF CTL effector FasL Killed target cell Target cell perforin gra nzym e B TNFRI trimerization TNF TNFRI trimerization T sejt sTNF T sejt sFasL FasL Fas trimerization Death domain Fas trimerization Antigen recognizing receptor CONSEQUENCE OF T CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSES Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize virus-infected or tumor cells Activated cytotoxic T-lymphocytes kill virus-infected or tumor cells